Biliary dyskinesia
Biliary Dyskinesia – Spaks Homeopathy Overview
Biliary Dyskinesia is a gallbladder condition where the organ works below normal efficiency (less than 33%). It is a type of motility disorder affecting the gallbladder and the sphincter of Oddi.
Also known as acalculous gallbladder disease, this condition occurs without gallstones. It may also be termed functional gallbladder disorder or impaired gallbladder emptying.
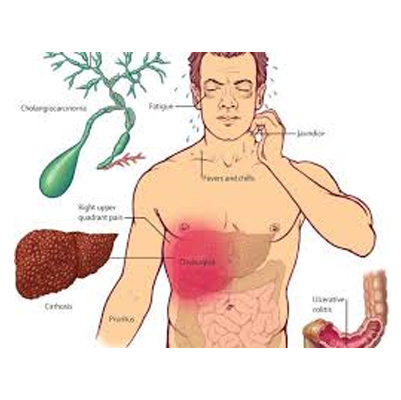
It is often found in both children and adults who experience biliary colic – pain in the upper right abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and intolerance to fatty foods. Because its symptoms resemble other digestive issues, it often goes undiagnosed.
Symptoms of Biliary Dyskinesia
-
Gallbladder attacks without gallstones
-
Right upper abdominal pain after eating
-
Gas and bloating
-
Frequent burping
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Fat intolerance
-
Symptoms similar to gallbladder colic
Spaks Homeopathy Approach
At Spaks Homeopathy, our treatment focuses on:
-
Relieving abdominal pain and discomfort
-
Restoring gallbladder motility and function
-
Improving digestion and fat tolerance
-
Offering safe, natural, and side-effect-free solutions
? Gentle healing for long-term relief with Spaks Homeopathy.
Do you also want me to make a very short summary version (4–5 lines) that you can directly use for quick awareness posts?
Cholecystitis
Overview – Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
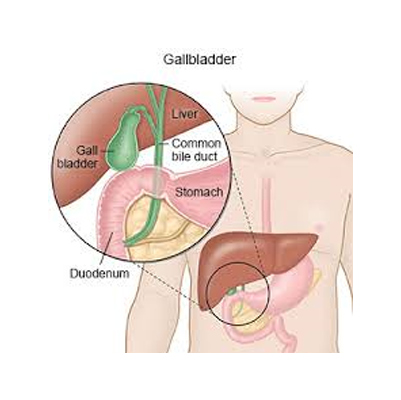
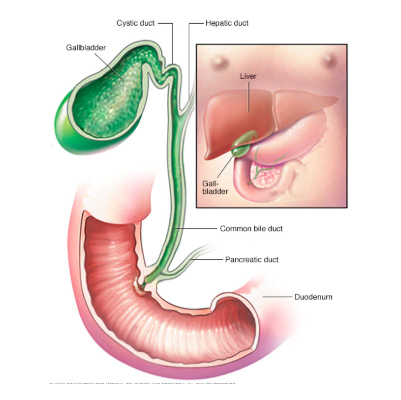
Cholelithiasis refers to the formation of stones (gallstones) inside the gallbladder – a small pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver on the right side of the abdomen.
The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid that helps in breaking down fats. When the chemical balance of bile is disturbed, solid particles can crystallize and form stones.
Gallstones can remain silent (without symptoms) for years, but when they block the bile ducts, they lead to pain, inflammation, or complications like cholecystitis, pancreatitis, or jaundice.
If untreated, repeated attacks can damage the gallbladder and digestive system.
Symptoms – Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
-
Sudden, intense pain in the right upper abdomen (biliary colic)
-
Pain radiating to the right shoulder or back
-
Abdominal bloating or indigestion
-
Nausea and vomiting after heavy or fatty meals
-
Fever and chills (if infection develops)
-
Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes if bile duct is blocked)
-
Loss of appetite and general discomfort
Effects if Untreated
-
Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder
-
Risk of gallbladder rupture (perforation)
-
Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas)
-
Bile duct obstruction leading to jaundice
-
Recurrent digestive problems and malabsorption
-
Increased risk of gallbladder cancer (in rare, long-term cases)
Spaks Homeopathy Treatment
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment for gallstones focuses on addressing the root cause, improving bile metabolism, reducing pain, and preventing recurrence without surgery.
Commonly Prescribed Homeopathic Medicines (as per individual case):
-
Chelidonium Majus – For gallstone pain radiating to the back and shoulder.
-
Lycopodium – For bloating, gas, and pain after heavy meals.
-
Carduus Marianus – For liver and gallbladder inflammation with nausea.
-
Calcarea Carb – For stone tendency in overweight or sluggish patients.
-
China (Cinchona) – For weakness and bloating due to digestive disturbances.
-
Nux Vomica – For gallbladder pain worsened by fatty/spicy foods and stress.
Why Choose Spaks Homeopathy?
-
Root-cause correction: Works on liver and gallbladder function, not just temporary relief.
-
Avoids surgery in many cases.
-
Safe, gentle, and side-effect free treatment.
-
Holistic healing: Improves digestion, metabolism, and overall well-being.
-
Personalized care: Every prescription is tailored to your body and constitution.
Address: E-38, Budh Vihar, Badarpur, New Delhi – 110044
Email: info@spakshomeopathy.com
Phone: +91 8700458818
Enlarged spleen
Enlarged Spleen (Splenomegaly)
Overview
An enlarged spleen (splenomegaly) often does not cause obvious symptoms and is usually discovered during a routine physical exam.
Normally, the spleen is not felt in adults, but when it enlarges, a doctor can feel it during examination.
To confirm the cause, doctors recommend blood tests and imaging (like ultrasound or CT scan).
Treatment focuses on correcting the underlying disease. Surgery to remove the spleen (splenectomy) is not the first choice, but it may be recommended if other treatments fail or complications develop.
Symptoms
-
Many people may have no symptoms
-
Pain or fullness in the left upper abdomen (may spread to left shoulder)
-
Feeling full quickly after eating small amounts (spleen pressing on stomach)
-
Anemia (low blood count)
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Frequent infections
-
Easy bleeding or bruising
Effects (If Untreated)
-
Severe anemia and weakness
-
Increased risk of frequent infections (because spleen helps immunity)
-
Low platelet count → excessive bleeding or bruising
-
Ruptured spleen (life-threatening emergency if the spleen bursts)
-
Poor quality of life due to weakness, tiredness, and pain
Treatment
1. Medications & Underlying Cause Management
-
Antibiotics → if infection is the cause
-
Anti-malarial drugs → if related to malaria
-
Chemotherapy / targeted therapy → if due to cancers like leukemia or lymphoma
-
Immunosuppressants → for autoimmune conditions
2. Lifestyle & Safety Measures
-
Avoid contact sports or heavy exercise (to prevent spleen rupture)
-
Take precautions against infections if the spleen is enlarged
-
Eat a balanced diet to manage anemia
3. Surgery (Splenectomy)
-
Done only if the spleen is severely enlarged, painful, or causing dangerous complications
-
After removal, patient needs vaccinations and preventive antibiotics, as immunity decreases
Gallbladder Polyp
Gallbladder Polyps – Overview (Spaks Homeopathy)
A gallbladder polyp is an abnormal growth projecting from the inner lining of the gallbladder. They are often detected incidentally during an abdominal ultrasound. Most gallbladder polyps are small and do not cause symptoms.
Polyps smaller than 1 cm are usually benign and harmless. However, larger polyps (greater than 1 cm) carry a higher risk of being malignant (cancerous). The likelihood of malignancy increases with size. For this reason, polyps larger than 1 cm are generally recommended for surgical removal.
Causes of Gallbladder Polyps
-
Abnormal growth of gallbladder lining cells
-
Chronic gallbladder inflammation
-
Cholesterol deposits in the gallbladder wall (cholesterol polyps)
-
Genetic predisposition in some individuals
-
Association with gallstones in certain cases
Symptoms of Gallbladder Polyps
Most gallbladder polyps are asymptomatic, but when symptoms occur, they may include:
-
Occasional pain in the right upper abdomen (right hypochondrium)
-
Nausea and discomfort after meals
-
Vomiting in some cases
-
Indigestion and bloating (less common)
Effects / Complications
-
Larger polyps can block bile flow, causing abdominal pain
-
Risk of malignant transformation in polyps larger than 1 cm
-
Gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis)
-
Rarely, association with gallbladder cancer
Homeopathic Treatment for Gallbladder Polyps (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy aims to improve gallbladder health, reduce inflammation, and manage associated digestive symptoms. Some commonly used remedies are:
-
Chelidonium Majus – for pain in the right upper abdomen and indigestion
-
Lycopodium Clavatum – for bloating, nausea, and right-sided abdominal pain
-
Carduus Marianus – for gallbladder and liver complaints with nausea
-
Cholesterinum – for gallbladder dysfunction associated with cholesterol deposits
-
Calcarea Carbonica – for tendency to polyp formation and digestive weakness
Note: Homeopathic remedies must be selected individually. Consultation with a qualified homeopathic physician is recommended for safe and effective treatment.
Gallstones
Overview
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that may type in your bladder.
Your bladder could be a tiny, pear-shaped organ on the correct facet of your abdomen, simply at a lower place y
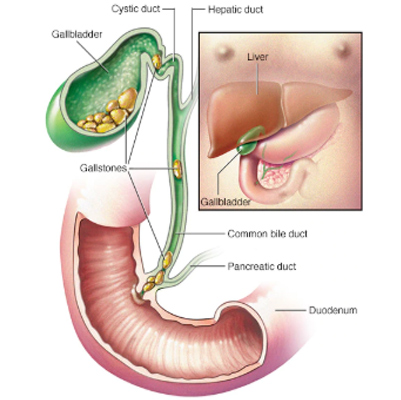
Gallstones – Overview (Spaks Homeopathy)
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid (bile) that form inside the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver, responsible for storing and releasing bile into the small intestine to aid digestion.
Gallstones can vary in size, ranging from a tiny grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people may develop only a single gallstone, while others can develop multiple stones at the same time. While many gallstones are silent and cause no symptoms, they may also lead to severe abdominal pain and complications when they block bile ducts.
Causes of Gallstones
-
Imbalance in the substances that form bile (cholesterol, bile salts, bilirubin)
-
Excess cholesterol in bile leading to crystallization
-
Poor gallbladder emptying causing bile stasis
-
Obesity or rapid weight loss
-
Family history of gallstones
-
Female gender, pregnancy, and hormonal changes (estrogen influence)
Symptoms of Gallstones
-
Severe, sudden pain in the upper right abdomen (gallbladder colic), sometimes radiating to the upper back or right shoulder
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Fever with chills (if infection develops)
-
Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes due to blocked bile flow)
-
Clay-colored stools or dark urine
-
Indigestion, bloating, or discomfort after fatty meals
Effects / Complications
-
Acute gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis)
-
Blockage of bile ducts leading to severe pain and infection
-
Pancreatitis (if gallstones block the pancreatic duct)
-
Chronic digestive issues
-
Increased risk of gallbladder cancer (rare but serious)
Homeopathic Treatment for Gallstones (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy helps in managing gallstone-related pain, improving bile flow, and reducing the tendency to form stones. Some commonly used remedies include:
-
Chelidonium Majus – for right-sided abdominal pain radiating to the back and shoulder
-
Lycopodium Clavatum – for bloating, nausea, and gallstone colic, worse in the evening
-
Carduus Marianus – for gallbladder and liver disorders with jaundice
-
Calcarea Carbonica – for individuals prone to gallstone formation with sluggish digestion
-
China (Cinchona Officinalis) – for weakness, gas, and bloating after gallstone attacks
Note: Remedies must be chosen according to individual symptoms. Consultation with a qualified homeopathic physician is recommended for safe and effective treatment.
our liver.
The bladder holds a digestive fluid known as digestive fluid that is discharged into your bowel. Gallstones direct size from as little as a grain of sand to as giant as a ball.
Some people develop only one gallstone, whereas others develop several gallstones at a similar time. People who expertise symptoms from their gallstones sometimes need bladder removal surgery.
Gallstones do not|that do not} cause any signs and symptoms generally don't want treatment.
Symptoms
Sudden and chop-chop deepening pain within the higher right portion of your abdomen
Back pain between your shoulder blades
Pain in your right shoulder
Nausea or vomiting
Sclerosing Cholangitis
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
Overview
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a progressive disease of the bile ducts, which carry bile from the liver to the small intestine.
-
In PSC, inflammation causes scarring inside the bile ducts, making them stiff and narrow.
-
Over time, this scarring can cause serious liver damage.
-
PSC progresses slowly in most patients, but it can lead to:
-
Liver failure
-
Recurrent infections in bile ducts
-
Tumors of the liver or bile ducts
-
-
Liver transplant is the only known cure for advanced PSC, although recurrence can occur in some transplanted livers.
Symptoms
Early symptoms may appear before a diagnosis, often detected during routine tests:
-
Fatigue
-
Itching
-
Pain in the right upper abdomen
-
Fever and chills
-
Night sweats
-
Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
-
Enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)
-
Weight loss
-
Yellowing of eyes and skin (jaundice)
Effects / Complications
-
Liver failure in advanced stages
-
Cholangitis (recurrent bile duct infections)
-
Biliary cirrhosis due to prolonged obstruction and scarring
-
Increased risk of liver and bile duct cancer
-
Fatigue, malnutrition, and vitamin deficiencies due to impaired bile flow
Treatment
1. Medical Management
-
Medications to relieve symptoms like itching (cholestyramine, rifampin)
-
Ursodeoxycholic acid may slow disease progression in some patients
-
Antibiotics for bile duct infections
-
Vitamin supplementation (A, D, E, K) for malabsorption
2. Endoscopic / Interventional Procedures
-
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) to dilate or stent narrowed bile ducts
-
Drainage of bile duct obstructions
3. Surgery / Transplant
-
Liver transplantation for end-stage PSC
-
Only definitive cure for advanced disease