Choking
Overview – Choking
Choking occurs when a piece of food, liquid, or an object becomes stuck in the throat or windpipe, blocking normal airflow.
In children, choking often happens when they put small objects or toys into their mouths. In adults, it is commonly due to eating or drinking too quickly, or sometimes inhaling fumes.
Most people experience choking at some point in their lives, and in many cases it is temporary and harmless. However, when the airway is completely blocked, choking can become life-threatening and requires immediate attention.
When choking occurs, the person may cough continuously to try to clear the airway. If the blockage remains, oxygen supply is cut off, which can quickly become dangerous.
Symptoms of Choking
-
Persistent coughing or gagging
-
Hand signals and panic (often pointing to the throat)
-
Sudden inability to speak
-
Clutching the throat (universal choking sign)
-
Wheezing or noisy breathing
-
Passing out (if blockage continues)
Effects of Choking
-
Damage or irritation to the throat and airway
-
Temporary loss of voice or difficulty speaking
-
Oxygen deprivation leading to unconsciousness
-
Risk of brain damage if oxygen supply is cut off for too long
-
Anxiety and fear after the episode, especially in children
Homeopathy Treatment – Spaks Approach
At Spaks Homeopathy, care for choking is focused on both emergency support and long-term prevention. While immediate medical intervention (like first aid and Heimlich maneuver) is crucial during a choking episode, homeopathy can play a role in:
-
Relieving irritation and inflammation in the throat after choking
-
Improving swallowing reflex in children or elderly individuals prone to choking
-
Reducing recurrent spasms or sensitivity in the throat
-
Supporting the respiratory system for faster recovery
Commonly prescribed remedies (based on individual symptoms):
-
Aconite – For sudden fear and shock after choking
-
Ipecac – For persistent gagging or choking with difficulty clearing the throat
-
Lachesis – For throat sensitivity and choking sensation, especially at night
-
Arsenicum Album – For weakness, anxiety, and breathing difficulty after choking
-
Belladonna – For throat spasms and sudden obstruction feeling
At Spaks, treatment is individualized after careful evaluation of the patient’s history, sensitivity, and triggers. Remedies are safe, gentle, and effective for children and adults alike.
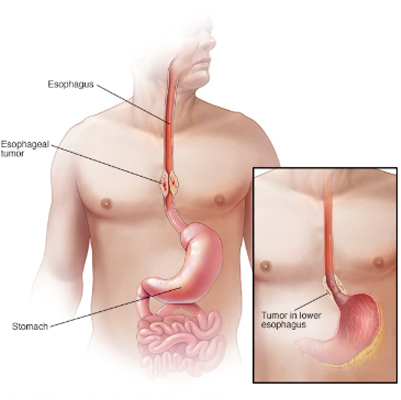
Dysphagia
Dysphagia (Difficulty Swallowing)
Overview
Dysphagia is a condition in which moving food or liquids from the mouth to the stomach takes more effort and time than normal. It may also cause pain while swallowing, and in severe cases, swallowing may become nearly impossible.
While an occasional problem swallowing (such as eating too quickly or not chewing properly) is usually harmless, persistent dysphagia often signals an underlying health issue that requires medical care.
This condition can occur at any age, though it is more common in older adults. Causes include neurological conditions, muscular problems, structural blockages, or complications from other diseases. Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of dysphagia include:
-
Pain while swallowing (odynophagia)
-
Inability to swallow in severe cases
-
Feeling of food stuck in the throat, chest, or behind the breastbone (sternum)
-
Drooling or difficulty controlling saliva
-
Hoarseness in voice
-
Regurgitation (bringing food back up)
-
Frequent heartburn or acid reflux
-
Food or stomach acid rising into the throat
-
Sudden, unexplained weight loss
-
Coughing or gagging during swallowing
Effects
If untreated, dysphagia can lead to:
-
Malnutrition and weight loss due to poor food intake
-
Dehydration from reduced liquid consumption
-
Respiratory infections or aspiration pneumonia, if food or liquids enter the airway
-
Emotional stress and anxiety while eating in public or social situations
-
Reduced quality of life due to persistent discomfort and fear of choking
Homeopathic Treatment (By Spaks)
Homeopathy aims to improve swallowing ability, relieve associated symptoms, and address underlying causes such as nerve weakness, muscular problems, or reflux. Remedies are selected based on the individual’s unique symptoms.
? Commonly used remedies include:
-
Belladonna – for painful swallowing with dryness and redness of throat.
-
Baryta Carbonica – for difficulty swallowing, especially in elderly people or those with weak muscles.
-
Lachesis – for choking sensation, constricted throat, or difficulty swallowing liquids.
-
Mercurius Solubilis – for painful, burning throat with increased salivation.
-
Phosphorus – for regurgitation and acid reflux with irritation in the throat.
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment is individualized, aiming to restore comfort in eating, strengthen immunity, and prevent complications naturally, without side effects.
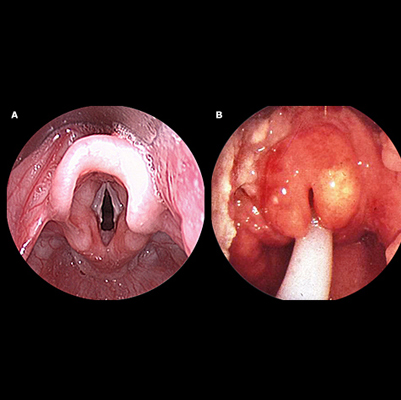
Epiglottitis
Epiglottitis – A Serious Airway Condition
Overview
Epiglottitis is a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the epiglottis — a small flap of tissue that covers the windpipe — becomes swollen and blocks airflow to the lungs.
Causes
The swelling of the epiglottis can be triggered by:
-
Burns from hot liquids
-
Throat injuries
-
Infections (bacterial or viral)
In the past, the most common cause in children was Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib), which also causes pneumonia, meningitis, and blood infections. Today, thanks to routine Hib vaccination, cases in children are rare, but epiglottitis can still occur at any age.
Emergency Warning: If epiglottitis is suspected, seek medical help immediately. Delay in treatment can lead to fatal complications.
Symptoms in Children
Symptoms usually develop rapidly within a few hours:
-
High fever
-
Severe sore throat
-
Stridor (high-pitched sound during breathing)
-
Painful or difficult swallowing
-
Drooling
-
Anxiety or restlessness
-
Relief when sitting upright or leaning forward
Symptoms in Adults
In adults, symptoms progress more slowly over a few days and may include:
-
Severe sore throat
-
Fever
-
Muffled or hoarse voice
-
Stridor (abnormal breathing sound)
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Drooling
-
Breathing difficulties
Effects if Untreated
If not treated promptly, epiglottitis can cause:
-
Complete airway blockage
-
Severe breathing difficulties
-
Low oxygen levels in the body
-
Respiratory failure
-
Death
Treatment Options
Conventional Treatment
-
Emergency hospitalization is required.
-
Oxygen support and airway management (sometimes intubation or tracheostomy) may be necessary.
-
Intravenous antibiotics for bacterial infection.
-
Pain relievers and fluids for supportive care.
Homeopathic Support (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy aims to reduce inflammation, improve immunity, and relieve associated symptoms naturally, without side effects. Common remedies include:
-
Belladonna – for sudden high fever, sore throat, and restlessness.
-
Hepar Sulph – for painful swallowing and sensitivity of the throat.
-
Kali Bichromicum – for thick mucus and hoarse voice.
-
Aconite – for sudden onset with anxiety and fear.
Why Spaks Homeopathy?
-
Gentle and side-effect free care
-
Focuses on root-cause healing and long-term prevention
-
Strengthens immunity and reduces recurrence of throat infections
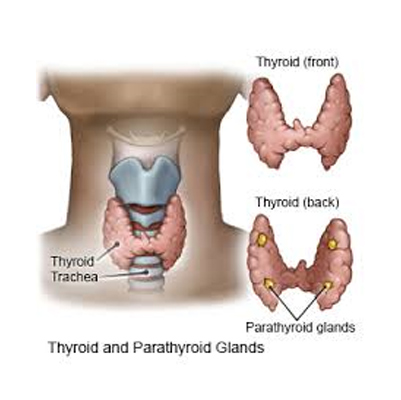
Goiter
Goiter – Overview
Goiter is an abnormal swelling of the thyroid gland, which appears as a lump in the neck. The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck. It produces thyroid hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism, and ensure the smooth functioning of the brain, heart, digestive system, and muscles.
Goiter can occur due to:
-
Overactive thyroid (Hyperthyroidism)
-
Underactive thyroid (Hypothyroidism)
-
Iodine deficiency
-
Autoimmune disorders (like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Graves’ disease)
-
Family history or genetic predisposition
-
Hormonal changes (common in pregnancy or menopause)
It may or may not be associated with abnormal thyroid hormone levels.
Goiter can affect people of any age – from newborn babies to elderly individuals. However, the risk is higher in:
-
Women (especially during pregnancy or menopause)
-
People above 40 years of age
-
Those with autoimmune diseases
-
People with family history of thyroid disorders
Symptoms of Goiter
Not every goiter causes symptoms. But when they do, they may include:
-
A visible swelling or lump in the neck (more noticeable while shaving or applying makeup)
-
A tightness in the throat
-
Coughing without obvious cause
-
Hoarseness in voice
-
Difficulty swallowing food
-
Difficulty breathing, especially when lying down
Effects / Complications if Untreated
-
Cosmetic discomfort (visible lump)
-
Difficulty in swallowing or breathing
-
Thyroid hormone imbalance → leading to hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
-
Risk of thyroid nodules or, rarely, thyroid cancer
Treatment of Goiter
The treatment depends on the cause, size of the goiter, hormone levels, and complications:
-
Medication – to normalize thyroid hormone levels (if overactive or underactive)
-
Hormone therapy – thyroid hormone supplements in hypothyroidism
-
Surgery (Thyroidectomy) – in cases of very large goiters causing pressure symptoms or suspicion of cancer
-
Homeopathic Treatment (Spaks Homeopathy) – Gentle, natural remedies that help regulate thyroid function, reduce swelling, and balance hormones.
Useful Homeopathic Remedies for Goiter:
-
Iodum – for enlarged thyroid with heat, weight loss, and restlessness
-
Spongia Tosta – for hard swelling in thyroid, hoarseness, and choking feeling
-
Calcarea Carb – for goiter in obese, sluggish individuals with excessive sweating
-
Lycopus Virginicus – for overactive thyroid with palpitations
-
Bromium – for hard nodular goiters, especially in fair-skinned people
Group A streptococci
Overview
Group A Streptococcus (GAS) are bacteria that spread mainly through:
-
Direct contact with saliva or nasal secretions of an infected person
-
Contact with infected wounds or skin sores
People with an active throat or skin infection are most likely to spread the bacteria. Carriers without symptoms are much less contagious.
Treating an infected person with antibiotics for at least 24 hours usually stops the spread. But it’s important to finish the full course of prescribed medicine.
Household items like plates, cups, or toys do not usually spread GAS bacteria.
Symptoms of GAS Pharyngitis (Strep Throat / Tonsillitis)
-
Persistent sore throat
-
Pain or irritation while swallowing
-
White patches / exudates on tonsils
-
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
-
Fever
-
Combination of sore throat + fever + white patches on tonsils are important, but not always definitive signs of strep throat.
Hyperthyroidism
Overview
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland (a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck) becomes overactive and produces too much of the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
These hormones play a key role in regulating the body’s metabolism — how cells use energy. When thyroid hormone levels are too high, the body’s metabolism speeds up, leading to a variety of symptoms.
If untreated, hyperthyroidism can cause serious health problems such as heart disease, osteoporosis, and thyrotoxic crisis (thyroid storm). Early diagnosis and proper treatment are important to manage the condition.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
-
Increased appetite
-
Nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
-
Restlessness or tremors (shaking hands/fingers)
-
Inability to concentrate
-
Weakness or muscle fatigue
-
Rapid or irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
-
Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
-
Fine, brittle hair or hair loss
-
Itching or skin changes
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Excessive sweating or heat intolerance
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
More frequent bowel movements
Effects of Hyperthyroidism
-
Cardiovascular problems: irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure, heart failure
-
Bone health issues: osteoporosis due to calcium loss
-
Eye problems (Graves’ disease): bulging eyes, irritation, double vision
-
Fertility & menstrual issues: irregular or absent periods in women, reduced fertility in men and women
-
Metabolic strain: rapid weight loss, muscle weakness, fatigue
-
Thyroid storm (severe untreated case): sudden worsening of symptoms → life-threatening
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
1. Medications
-
Antithyroid drugs (e.g., Methimazole, Propylthiouracil) – reduce thyroid hormone production.
-
Beta-blockers – manage rapid heartbeat, tremors, and anxiety (do not affect hormone levels).
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy
-
Used to shrink or destroy overactive thyroid cells.
-
Commonly used when medications are ineffective or not tolerated.
3. Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
-
Partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland in severe or recurrent cases.
-
May require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement after surgery.
4. Lifestyle & Supportive Care
-
Eat a balanced diet and avoid excessive iodine (e.g., kelp, certain supplements).
-
Manage stress and get enough rest.
-
Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels with your doctor.
Key Point: Hyperthyroidism speeds up your body’s metabolism. With timely diagnosis and proper treatment, most people can manage symptoms effectively and prevent long-term complications.
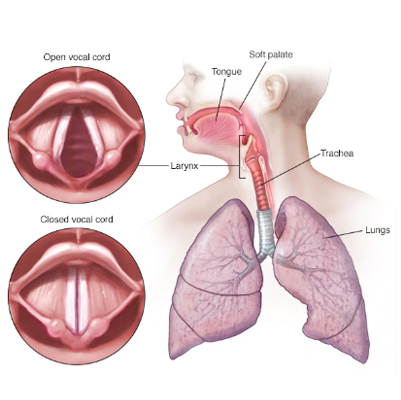
Laryngitis
Laryngitis
Overview
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx (voice box), usually caused by infection, vocal strain, or irritation. Inside the larynx are the vocal cords, which normally open and close smoothly, producing sound through their movement and vibration.
When inflamed or irritated, the vocal cords swell, leading to distortion in sound. This makes the voice hoarse or, in severe cases, temporarily lost.
Laryngitis may be acute (short-term), often due to viral infection or overuse of the voice, or chronic (long-term), which can be linked to irritants, smoking, acid reflux, or more serious conditions.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of laryngitis include:
-
Hoarseness
-
Weak voice or voice loss
-
Tickling or raw sensation in the throat
-
Sore throat
-
Dry throat
-
Dry cough
Effects
If not managed, laryngitis can lead to:
-
Persistent voice changes
-
Difficulty speaking or communicating
-
Throat discomfort affecting daily activities
-
In chronic cases, it may indicate underlying conditions such as vocal cord nodules, polyps, or even cancer.
Treatment
Most cases of acute laryngitis improve within a week with self-care. Management includes:
-
Voice rest: Avoid talking loudly, shouting, or whispering
-
Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to soothe the throat
-
Humidified air: Use a humidifier or inhale steam to keep the throat moist
-
Avoid irritants: Stay away from smoke, alcohol, and excessive caffeine
-
Medical treatment: Antibiotics if bacterial infection is suspected, corticosteroids for severe inflammation, or treatment of underlying conditions (e.g., reflux, allergies)
-
For chronic laryngitis: Address the root cause such as acid reflux, smoking, or workplace irritants
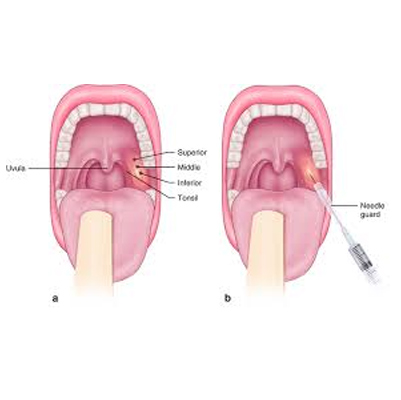
Peritonsillar
Peritonsillar Abscess
Overview
A peritonsillar abscess is a bacterial infection that usually develops as a complication of untreated strep throat or tonsillitis. It involves a pus-filled pocket forming near one of the tonsils.
Peritonsillar abscesses are most common in children, adolescents, and young adults, often occurring during the winter months when infections like strep throat and tonsillitis are more prevalent.
If left untreated, the abscess can spread to surrounding tissues and lead to serious complications, making prompt medical care essential.
Symptoms
-
Severe sore throat, usually worse on one side
-
Swelling of the face or neck
-
Difficulty opening the mouth fully (trismus)
-
Trouble swallowing or swallowing saliva (drooling)
-
Fever and chills
-
Muffled voice or “hot potato” voice
-
Headache
-
Swollen glands in the throat and jaw, tender to touch
-
Ear pain on the same side as the affected tonsil
-
Bad breath
-
Redness and infection in one or both tonsils
Effects
-
Severe pain and difficulty eating, drinking, or speaking
-
Risk of spread of infection to deeper neck structures
-
Dehydration due to difficulty swallowing
-
Possible airway obstruction in severe cases
-
General fatigue, malaise, and fever from systemic infection
Treatment
1. Medical Intervention (Emergency Care if Needed)
-
Drainage of the abscess: via needle aspiration, incision, or surgical removal
-
Antibiotics: usually intravenous (IV) or oral to fight the bacterial infection
-
Pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications
2. Supportive Care at Home (Post-Treatment)
-
Rest and hydration
-
Soft or liquid diet until swallowing improves
-
Warm saltwater gargles to soothe the throat
-
Good oral hygiene to prevent reinfection
3. Preventive Measures
-
Prompt treatment of strep throat or tonsillitis
-
Avoid sharing utensils, drinks, or close contact when infected
-
Regular hand washing to reduce bacterial spread