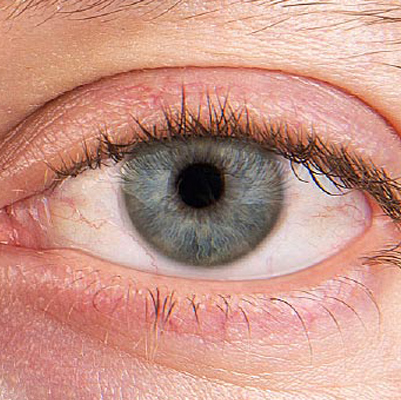
Jaundice
Itchy Skin (Pruritus)
Overview
Itchy skin, or pruritus, is an irritating sensation that makes you want to scratch. It can be mild, short-lived, or severe and persistent, interfering with daily life. Dry skin is one of the most common causes, especially in older adults.
Itchy skin may look normal or show visible changes like redness, bumps, or rough patches. Repeated scratching often worsens the condition, leading to skin damage, bleeding, or infections.
Relief often requires a mix of self-care, medical treatment, and addressing the root cause.
Symptoms
-
Localized itching (small areas like arms/legs) or generalized itching (whole body)
-
Redness
-
Bumps, spots, or blisters
-
Dry, cracked skin
-
Thickened, leathery, or scaly skin from scratching
Effects
If untreated, itchy skin can lead to:
-
Sleep disturbances due to constant discomfort
-
Skin damage (cuts, bleeding, sores)
-
Secondary bacterial infections from scratching
-
Emotional distress, irritability, or anxiety
-
In chronic cases, permanent skin changes (thick, dark patches or scars)
Treatment
Self-care/Home Remedies:
-
Use fragrance-free moisturizers several times a day
-
Bathe with lukewarm water (avoid hot water)
-
Use gentle, non-soap cleansers
-
Apply cold compresses for relief
-
Keep nails short to reduce skin damage from scratching
Medical Treatments (depending on cause):
-
Medicated creams/ointments (corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors)
-
Antihistamines (for allergy-related itching)
-
Anti-itch lotions with menthol, camphor, or pramoxine
-
Phototherapy (light treatment for chronic itching)
-
Treatment of underlying conditions (eczema, psoriasis, liver/kidney issues, thyroid problems, etc.)
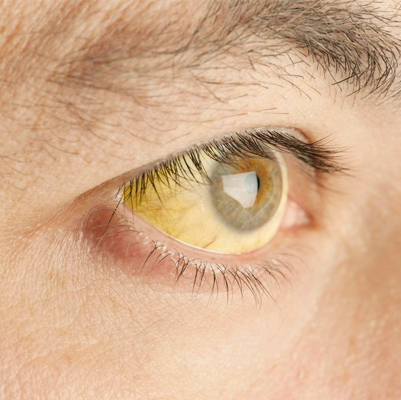
Astigmatism
Astigmatism – Spaks Homeopathy Overview
Astigmatism is an eye condition that occurs when the natural shape of the eye is slightly irregular. Normally, the eyeball is round like a ball, allowing light to bend evenly and create a clear vision. But in astigmatism, the eye takes more of an oval shape — like a football or the back of a spoon. This irregular curve bends light unevenly, causing only part of an object to be focused, while the rest appears blurred or distorted.
People with astigmatism often experience blurry, fuzzy, or wavy vision at both near and far distances.
Symptoms of Astigmatism
-
Blurred or distorted vision
-
Difficulty seeing clearly at night
-
Frequent eye strain or discomfort
-
Habitual squinting to see clearly
-
Irritation or tiredness in eyes
-
Headaches due to constant focusing effort
At Spaks Homeopathy, our natural and holistic remedies aim to:
Improve eye health
Reduce strain and discomfort
Support clear, focused vision
Work gently without side effects
With the right homeopathic treatment, astigmatism can be effectively managed to bring lasting relief and sharper vision.
Would you like me to also create a short social media-style post (with emojis and catchy lines) for Astigmatism from Spaks?
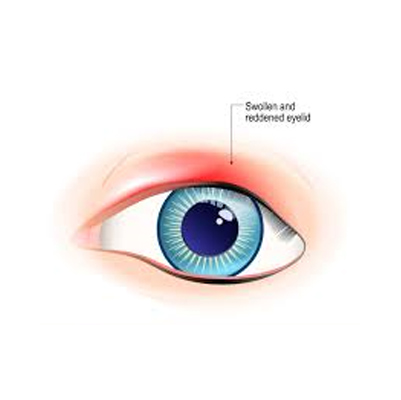
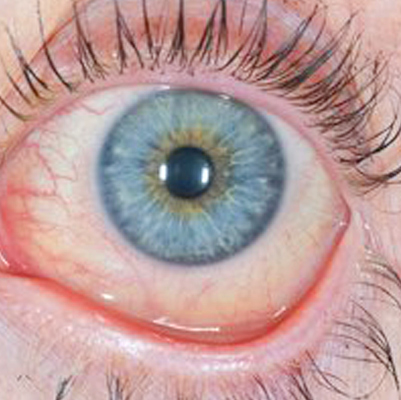
Blepharitis
Overview
Blepharitis is a common eye condition that affects the eyelid margins and may sometimes occur along with conjunctivitis. It can start in early childhood and persist as a chronic problem throughout life, or it may develop later.
This condition involves inflammation around the base of the eyelashes. While the exact causes of chronic blepharitis are not fully understood, it is clear that poor hygiene is not the reason behind it.
Symptoms of Blepharitis
-
Red, irritated eyes
-
Feeling of a foreign particle in the eyes
-
Itching or burning sensation
-
Swelling of the eyelids
-
Flaking or crusting around the lashes
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Loss of eyelashes in some cases
Would you like me to also add a Causes & Treatment (including homeopathy options) section to make it more detailed, like the previous notes?
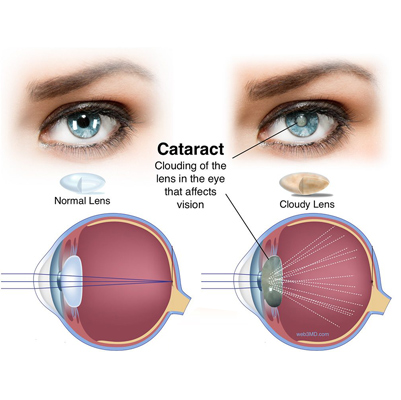
Cataract
Cataract – Spaks Homeopathy
Overview
A cataract is the clouding of the eye’s natural lens, which makes vision unclear or blurred. It can affect one or both eyes and is especially common in older people.
For someone with cataracts, vision may feel like looking through a frosted or foggy window. This cloudy vision can make it difficult to read, drive (especially at night), or recognize faces.
Cataracts usually develop slowly and may not disturb vision in the early stages. However, over time, they can significantly interfere with daily activities.
In the beginning, brighter lighting or corrective glasses may help. If cataracts progress and impair normal activities, surgery is often recommended. Cataract surgery is a safe and effective procedure for restoring vision.
Signs of a Cataract
-
Cloudy or blurry vision
-
Seeing halos or glare around lights
-
Poor night vision
-
Double vision in one eye
-
Colors appearing dull or faded
Spaks Homeopathy View:
Homeopathic remedies may help in the early stages of cataract by slowing down progression, improving eye health, and supporting overall vision, reducing the need for early surgery in some cases.
Color Blindness
Overview
Color blindness is not true blindness but rather a deficiency in the way the eyes perceive colors. People with this condition have difficulty distinguishing between certain shades, most commonly red and green, or sometimes blue and yellow. In rare cases, individuals may only see in shades of black, white, and gray (total color vision deficiency).
While it usually does not cause complete vision loss, color blindness can impact daily activities such as learning, reading, or recognizing signals and patterns. It is generally inherited and present from birth, though it may also develop later due to eye diseases, aging, or certain medications.
Symptoms
-
Low attention span during coloring or reading tasks involving colors
-
Denial or unawareness of color recognition problems
-
Difficulty identifying red or green pencils (or colors containing these shades such as purple or brown)
-
Struggles in distinguishing between shades of similar hue
-
Increased difficulty in poor lighting or with small color details
-
Sensitivity to bright lights
-
Reading or recognition problems with colored text on colored backgrounds
Effects if Untreated
-
Learning difficulties in children, especially in early school years when color-coded material is used
-
Safety risks due to difficulty distinguishing traffic signals or warning labels
-
Occupational limitations in careers requiring accurate color vision (pilots, electricians, designers, etc.)
-
Emotional effects, such as frustration, embarrassment, or lack of confidence in social/academic activities
Treatment
There is currently no cure for inherited color blindness, but supportive treatments and aids can improve quality of life:
-
Special color-filter glasses or contact lenses to enhance contrast between colors
-
Digital apps and software tools to assist with identifying colors
-
Adaptive teaching strategies in schools, such as using labels instead of relying on color codes
-
Treating underlying causes (if color blindness is acquired) like managing diabetes, glaucoma, or cataracts
-
Occupational guidance to help patients choose careers where color vision deficiency has minimal impact
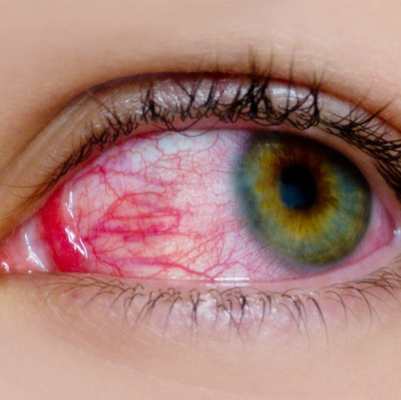
Conjunctivitis
Overview
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye) is an infection or inflammation of the conjunctiva – the thin, transparent membrane that covers the white part of the eyeball and lines the eyelid.
When small blood vessels in the conjunctiva become inflamed, they become more visible, giving the eye a reddish or pinkish appearance.
It can be caused by:
-
Infections: Viruses, bacteria
-
Non-infectious causes: Allergies, dust, smoke, fumes, or irritants
Conjunctivitis is usually mild but can be highly contagious in infectious cases. Early treatment and hygiene can prevent complications.
Symptoms
-
Redness in one or both eyes
-
Itchiness in one or both eyes
-
Gritty or burning sensation in the eyes
-
Sticky discharge that may form crusts overnight, causing difficulty in opening the eyes in the morning
-
Excessive tearing or watery eyes
-
Swelling of eyelids in some cases
-
Sensitivity to light (photophobia) in severe cases
Effects
-
Discomfort and irritation in daily activities (reading, working, screen use)
-
Risk of spreading to family members or classmates (if infectious)
-
Temporary blurred vision
-
Difficulty wearing contact lenses
-
If untreated or severe: may cause complications like corneal ulcers, keratitis, uveitis, or corneal perforation
Treatment
Conventional Treatment
-
Viral Conjunctivitis: Usually self-limiting, cold compress and artificial tears help relieve symptoms
-
Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Antibiotic eye drops or ointments
-
Allergic Conjunctivitis: Antihistamine or anti-inflammatory eye drops
-
Maintain good hygiene: Wash hands, avoid touching/rubbing eyes, avoid sharing towels, eyewear, or cosmetics
Spaks Homeopathy Treatment
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment is focused on relieving discomfort, reducing recurrence, and improving eye immunity naturally. Remedies are prescribed based on individual symptoms:
-
Euphrasia (Eyebright) – for burning, redness, and watery eyes with sensitivity to light
-
Belladonna – for intense redness, throbbing eye pain, and photophobia
-
Pulsatilla – for thick yellow-green discharge and itching, worse in warm rooms
-
Apis mellifica – for swollen eyelids with stinging pain and watery discharge
-
Argentum nitricum – for mucopurulent discharge with sticky eyelids in the morning
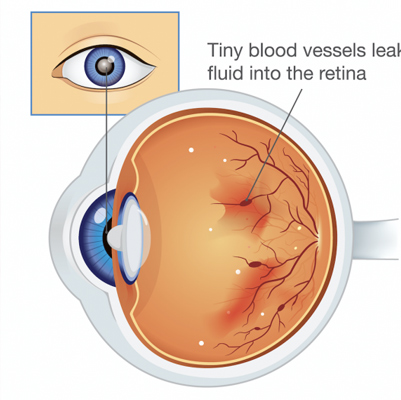
Diabetic Retinopathy
Overview
Diabetic Retinopathy is a serious eye complication of diabetes that can eventually lead to vision loss or blindness.
It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye). These vessels may become weak, leak blood or fluid, or grow abnormally, leading to impaired vision.
The condition usually affects both eyes and can progress silently without symptoms in the early stages. Regular eye checkups are crucial for early detection and prevention.
Signs & Symptoms
-
Floating dark spots or cobweb-like shapes in vision (floaters)
-
Blurred or distorted vision
-
Blocked or hazy vision
-
Difficulty seeing at night
-
Loss of central vision in advanced cases
Effects / Complications
If untreated, diabetic retinopathy may cause:
-
Macular edema → swelling in the retina, leading to vision loss
-
Retinal detachment → pulling away of the retina, causing permanent blindness
-
Glaucoma → increased eye pressure, damaging the optic nerve
-
Progressive blindness if blood vessel damage worsens
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Spaks Homeopathy focuses on preventing progression, strengthening blood vessels, and supporting retinal health naturally.
? Key Remedies Used in Spaks Homeopathy:
-
Phosphorus – For blurred vision, retinal weakness, and sensitivity to light.
-
Belladonna – For sudden vision changes, eye congestion, and pain.
-
Arnica Montana – For retinal hemorrhage (bleeding in the retina).
-
China (Cinchona Off.) – For weakness after blood loss in the eye.
-
Syzygium Jambolanum (supportive) – Helps regulate blood sugar levels to protect the eyes.
-
Crotalus Horridus – For retinal hemorrhages with hazy or blocked vision.
Dry eyes
Overview
Tears are essential to keep the eyes moist, healthy, and comfortable. Dry eye syndrome is a common condition that occurs when the eyes either do not produce enough tears, the tears evaporate too quickly, or there is an imbalance in the composition of tears (mucus, water, and oils).
This condition may develop due to aging, systemic diseases (such as Sjögren’s syndrome, arthritis, lupus, thyroid disorders), or lifestyle factors like prolonged screen use, pollution, exposure to sunlight, cigarette smoke, and dry environments.
If not managed properly, dry eyes can significantly impact quality of life and may even lead to serious complications such as corneal ulcers, scarring, and vision loss.
Symptoms
Dry eyes usually affect both eyes and may present with:
-
Stinging, burning, or scratchy sensation
-
Stringy mucus in or around the eyes
-
Eye redness
-
Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
-
Feeling of “something in the eye” (foreign body sensation)
-
Blurred vision or eye fatigue
-
Itchy eyes
-
Watery eyes (paradoxical reflex tearing due to irritation)
-
Difficulty wearing contact lenses
-
Trouble with nighttime driving
Effects
If untreated, dry eyes can cause:
-
Persistent discomfort and irritation
-
Recurrent eye infections
-
Inflammation of the eye surface
-
Damage to the cornea (ulcers, scarring)
-
Long-term risk of partial vision loss
Treatment & Management
The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms, improve tear quality, and protect the eyes.
? Lifestyle & Home Care
-
Limit screen time and take frequent breaks
-
Blink regularly, especially while reading or working on computers
-
Wash eyes frequently with clean water
-
Stay hydrated and maintain a balanced diet (rich in omega-3 fatty acids)
-
Use a humidifier indoors to prevent dryness
-
Wear protective glasses when outdoors
? Medical Care
-
Artificial tears (eye drops) – mainstay treatment to keep eyes lubricated
-
Lubricating gels/ointments for more severe dryness
-
Anti-inflammatory eye drops in autoimmune or severe cases
-
Treating underlying diseases like thyroid imbalance, arthritis, or Sjögren’s syndrome