Eye infections
Overview
Eye infections occur when harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi invade any part of the eyeball or surrounding area. This may involve the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye) or the conjunctiva (the thin, moist membrane covering the outer eye and inner eyelids).
Infections can affect one or both eyes and may range from mild irritation to more serious conditions if left untreated.
Symptoms of Eye Infections
-
Pink or red eyes
-
Eye pain or discomfort
-
Eye discharge (watery, sticky, or pus-like)
-
Excessive tearing (watery eyes)
-
Dryness or irritation
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Swelling of the eyes or eyelids
-
Itching or burning sensation
-
Blurred or hazy vision
Effects of Eye Infections
-
Constant discomfort and irritation
-
Temporary or long-term vision problems if untreated
-
Difficulty in daily activities due to blurred vision
-
Risk of spreading infection to the other eye or others
-
Emotional stress due to appearance of red/swollen eyes
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Spaks Homeopathy provides a safe and natural approach to treating eye infections without harmful side effects. Instead of just suppressing symptoms, homeopathy works by strengthening the body’s immunity and reducing the tendency for recurring infections.
Benefits of Spaks Homeopathic Treatment:
-
Reduces redness, swelling, and pain in the eyes
-
Controls excessive watering or dryness
-
Relieves itching, irritation, and burning sensations
-
Improves overall eye health and prevents recurrence
-
Boosts immunity for long-term protection
-
Gentle, safe, and suitable for all age groups
At Spaks, remedies are prescribed after a detailed case study to ensure personalized treatment for effective recovery.
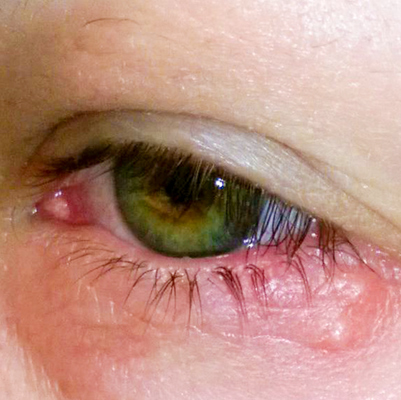
Eye injuries
Overview
Eye injuries can range from minor irritations to serious conditions that may cause permanent vision loss or, in extreme cases, loss of the eye itself.
Even seemingly trivial injuries, such as shampoo entering the eye, should not be ignored, as some injuries can have long-term effects. Eye injuries may occur at home, workplace, or during sports activities.
It is important to treat all eye injuries as potential emergencies and consult an eye specialist immediately. Early care can prevent complications and preserve vision.
Symptoms of Common Eye Injuries
-
Severe eye pain
-
Redness or pinkness in the eye
-
Decreased vision or blurriness
-
Conjunctivitis (eye inflammation)
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Eye drainage or discharge
-
Abnormal pH levels (chemical injuries)
-
Surface abrasions on the eye (scratches)
-
Excessive tearing
-
Watery discharge
-
Eye irritation or burning sensation
Effects of Eye Injuries
-
Short-term or long-term visual impairment
-
Persistent pain and discomfort
-
Increased risk of eye infections
-
Corneal damage or scarring
-
Emotional stress and difficulty in daily activities
-
In severe cases, irreversible blindness
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Spaks Homeopathy provides a gentle and holistic approach to managing eye injuries, focusing on reducing pain, promoting healing, and preventing long-term complications.
Benefits of Spaks Homeopathic Treatment:
-
Relieves pain, redness, and irritation
-
Helps repair eye surface abrasions naturally
-
Reduces sensitivity to light
-
Controls excessive tearing and discharge
-
Strengthens eye tissues for faster recovery
-
Safe, non-invasive, and without harmful side effects
At Spaks, treatment is tailored to the individual’s condition after a detailed consultation, ensuring personalized healing and long-term eye protection.
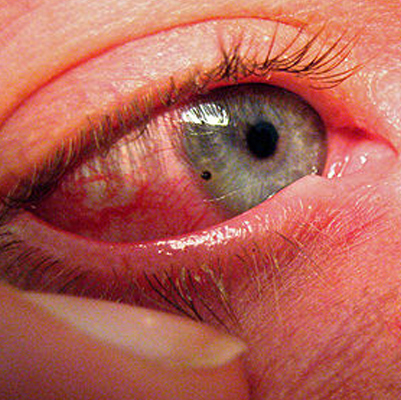
Eye Redness
Overview
There are many possible causes of red eyes, ranging from minor irritation to serious medical conditions. While redness alone is often less concerning, when it is accompanied by eye pain, discharge, or vision changes, it may indicate an emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
Red or bloodshot eyes occur when the tiny blood vessels on the surface of the eye enlarge and fill with blood. This can result from inadequate oxygen supply to the cornea or the tissues covering the eye.
Although red eyes are sometimes linked to simple causes such as dryness, allergies, or fatigue, they can also be a sign of infections or more serious eye diseases.
Symptoms of Red Eyes
-
Itching in the eye
-
Excessive tearing or watery eyes
-
Visible redness of one or both eyes
-
Eye discharge (watery, sticky, or pus-like)
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Blurred or poor vision
-
Gritty or sandy feeling in the eye
Effects of Red Eyes
-
Constant discomfort and irritation
-
Reduced clarity of vision
-
Risk of developing chronic eye conditions if left untreated
-
Possible spread of infection to the other eye
-
Emotional or social stress due to eye appearance
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Spaks Homeopathy offers a natural and safe approach to treating red eyes by addressing the underlying cause rather than just suppressing symptoms. Remedies are chosen individually after a detailed consultation to ensure the most effective care.
Benefits of Spaks Homeopathic Treatment:
-
Relieves itching, burning, and irritation
-
Reduces redness and watery discharge
-
Controls sensitivity to light
-
Improves overall eye health and comfort
-
Helps prevent recurrence of infections or allergies
-
Gentle, side-effect free, and suitable for all age groups
With Spaks Homeopathy, patients can achieve long-term relief, healthier eyes, and improved vision comfort.
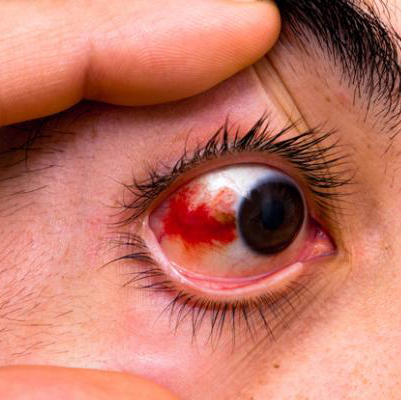
Floaters
Eye Redness and Eye Floaters – Overview (Spaks Homeopathy)
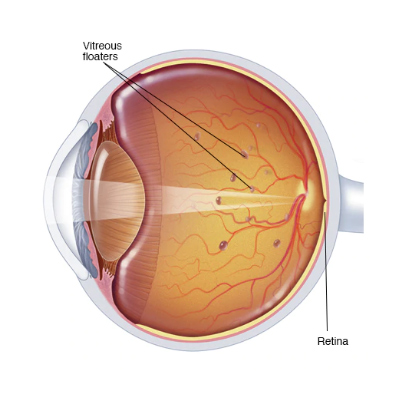
Eye redness usually occurs due to swollen or dilated blood vessels on the surface of the eye, giving the eye a reddish or unhealthy look. Another common condition affecting vision is eye floaters – tiny shapes or spots that appear to drift across your field of vision.
Floaters may look like black or gray specks, strings, or cobweb-like structures that move when you move your eyes. They are most often caused by age-related changes in the vitreous, the jelly-like substance inside the eyes. With age, the vitreous becomes more liquid, and microscopic fibers clump together, casting shadows on the retina, which appear as floaters.
While floaters are usually harmless, a sudden increase in floaters, light flashes, or partial loss of vision can be a sign of a serious eye emergency requiring immediate medical care.
Causes of Eye Redness and Floaters
-
Swelling or dilation of blood vessels in the eye
-
Irritation due to dust, allergy, or infection
-
Age-related changes in the vitreous (most common)
-
Eye injury or trauma
-
Retinal tear or detachment (serious condition)
Symptoms of Eye Floaters
-
Small dark spots, specks, or string-like shapes in vision
-
Spots that move when the eye moves, and dart away when looked at directly
-
Floaters most visible against bright backgrounds (blue sky, white wall)
-
Cobweb-like shapes drifting slowly across the line of sight
-
Sometimes associated with flashes of light or vision loss (warning sign)
Effects / Complications
-
Persistent disturbance in clear vision
-
Difficulty focusing on bright or uniform surfaces
-
Stress and eye strain due to constant floaters
-
Retinal detachment (in severe cases) leading to permanent vision loss
Homeopathic Treatment for Eye Redness and Floaters (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy helps by reducing eye irritation, improving blood circulation, and strengthening the eye tissues. Commonly used remedies include:
-
Belladonna – for redness, irritation, and throbbing eye pain
-
Euphrasia (Eyebright) – for watery eyes, redness, and sensitivity to light
-
Phosphorus – for floaters with flashes of light or blurred vision
-
Silicea – for chronic eye weakness and black spots in vision
-
Nux Vomica – for eye strain caused by overwork or stress
Glaucoma
Overview
Glaucoma is an eye disease that can cause vision loss or blindness. With glaucoma, fluid builds up in the eye, which puts pressure on the back of the eye. This pressure injures the optic nerve and causes vision loss. Side vision is often affected first, followed by front vision.
Types of Glaucoma There are two main types of glaucoma:
• Open-angle glaucoma often has no signs until it reaches an advanced stage. The pressure slowly damages the optic nerve over time. This affects both eyes but you may have signs in one eye first.
• Angle-closure glaucoma has a very fast rise in pressure and sudden signs. Permanent vision loss can occur within one day so it is very important to seek medical care right away.
Signs Glaucoma may have no signs until there is vision loss.
• Blurred vision
• Halos around lights
• Loss of peripheral or side vision
• Tunnel vision
• Red eyes
• Severe eye pain
• Nausea and vomiting
Keratitis
Keratitis
Overview
Keratitis is the inflammation of the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped tissue at the front of the eye that covers the pupil and iris.
It may or may not be caused by an infection:
-
Non-infectious keratitis can result from minor eye injuries, wearing contact lenses too long, or a foreign object in the eye.
-
Infectious keratitis can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites.
Prompt treatment is very important. Mild to moderate cases usually respond well to treatment without lasting damage. However, if left untreated, keratitis can lead to serious complications and permanent vision loss.
Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of keratitis include:
-
Redness of the eye
-
Eye pain
-
Excess tearing or discharge
-
Difficulty opening the eyelid due to pain or irritation
-
Blurred vision
-
Decreased vision
-
Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
-
Feeling like something is stuck in the eye (foreign body sensation)
Effects
If untreated or severe, keratitis can cause:
-
Permanent scarring of the cornea
-
Vision loss or blindness
-
Chronic eye pain
-
Corneal ulcers (open sores on the cornea)
-
Spread of infection inside the eye
Treatment
The treatment depends on the cause:
-
Bacterial keratitis → Treated with antibiotic eye drops.
-
Viral keratitis → Antiviral eye drops or oral medication (commonly for herpes simplex virus).
-
Fungal keratitis → Antifungal eye drops or oral antifungal drugs.
-
Parasitic keratitis (e.g., Acanthamoeba) → Special antiparasitic medications.
-
Non-infectious keratitis → Lubricating eye drops, avoiding contact lenses, and treating underlying causes.
General care:
-
Avoid contact lenses until fully healed
-
Use prescribed eye drops regularly
-
Protect eyes from bright light with sunglasses
-
Seek immediate medical care if symptoms worsen
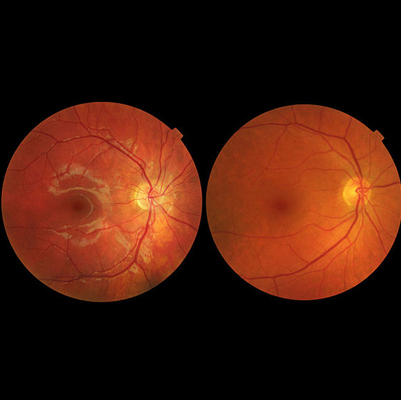
Macula Degeneration
Overview
The macula is the central part of the retina — the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. It is responsible for sharp, straight-ahead vision, which allows us to read, drive, and see fine details.
When the macula deteriorates, it leads to a condition called macular degeneration. The most common type is Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD), usually occurring in people over 60 years. AMD can be dry (gradual progression) or wet (rapid and severe vision loss due to abnormal blood vessels under the retina).
Symptoms
-
Seeing floating specks or cobwebs
-
Blurred or distorted vision (straight lines appear wavy)
-
Difficulty recognizing faces
-
Defects in side (peripheral) vision
-
Central vision loss, making reading and driving difficult
-
Dark or empty spots in central vision
Effects (If Untreated)
-
Progressive central vision loss (permanent in severe cases)
-
Difficulty with daily activities like reading, writing, or driving
-
Risk of blindness in advanced wet AMD
-
Emotional effects such as depression, anxiety, and loss of independence
Treatment
Conventional Treatment
-
No cure for AMD, but treatments can slow progression:
-
Anti-VEGF injections (ranibizumab, aflibercept) for wet AMD to stop abnormal blood vessel growth
-
Laser therapy to seal leaking blood vessels
-
Photodynamic therapy for selective destruction of abnormal vessels
-
-
Nutritional supplements (AREDS2 formula): high doses of vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, copper, lutein, and zeaxanthin may slow dry AMD progression
-
Low-vision aids (magnifying glasses, special lenses) to improve quality of life
Lifestyle & Prevention
-
Stop smoking (major risk factor)
-
Eat leafy green vegetables, fish, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids
-
Wear sunglasses to protect against UV rays
-
Regular eye checkups after age 50
Homeopathic Support (Complementary)
(To be used under professional guidance, not as replacement for medical care)
-
Phosphorus – for blurred and weak vision with sensitivity to light
-
Belladonna – for sudden visual disturbances and distorted images
-
Nux Vomica – for eye strain from overwork and central vision weakness
-
Gelsemium – for dim vision with dizziness
Optic Atrophy
Overview
Optic atrophy is a condition that occurs when the optic nerve, which transmits visual information from the eye to the brain, becomes damaged and begins to waste away (atrophy).
It is not a disease in itself but rather a sign of an underlying disorder that has injured the optic nerve. This damage may result from various causes, including poor blood flow, trauma, inflammation, or neurological conditions.
Optic atrophy often leads to vision problems and, in severe cases, may cause partial or complete blindness.
Symptoms of Optic Atrophy
Changes in vision are the hallmark of optic atrophy. Common symptoms include:
-
Blurred or dim vision
-
Difficulty with peripheral (side) vision
-
Problems distinguishing colors (color vision defects)
-
Reduced visual sharpness (acuity)
-
Loss of contrast sensitivity (difficulty seeing in low light or distinguishing shades)
-
In advanced cases: tunnel vision or blindness
Effects
-
Progressive, permanent loss of vision (since optic nerve fibers do not regenerate)
-
Difficulty with daily activities such as reading, driving, or recognizing faces
-
Emotional and psychological effects such as anxiety, stress, or depression due to vision loss
-
May be a sign of serious neurological or systemic diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, glaucoma, brain tumor, or stroke
Treatment
There is currently no cure to reverse optic atrophy, since damaged nerve fibers cannot be restored. However, treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause and preventing further damage:
-
Medications
-
Corticosteroids or immunosuppressants (for inflammation or autoimmune causes)
-
Drugs to lower intraocular pressure (in glaucoma-related cases)
-
-
Surgical / Medical Interventions
-
Treating brain tumors, infections, or vascular problems that may be causing optic nerve damage
-
Managing systemic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension that may affect blood flow to the optic nerve
-
-
Supportive Care
-
Vision aids (magnifiers, special glasses, adaptive devices)
-
Occupational therapy to help patients adapt to vision loss
-
Counseling and support groups for psychological well-being
-
-
Prevention & Management
-
Regular eye exams for early detection of eye and neurological diseases
-
Controlling chronic conditions (diabetes, hypertension)
-
Protecting eyes from injury and toxins
-