Alopecia areata
Alopecia Areata – An Overview
Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s own immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Hair usually falls out in small, round patches that may be unnoticeable at first. Over time, these patches may join together, making the condition more visible.
Although it most commonly affects the scalp, sudden hair loss may also occur on the eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, and other parts of the body. The condition can develop suddenly, improve, and then return again after months or even years.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
-
Sudden hair loss in small patches on the scalp
-
Patches may be a few centimeters wide or smaller
-
Hair loss may spread and appear in multiple areas
-
Can affect eyebrows, eyelashes, beard, or other body hair
-
Some people lose hair in only a few spots, while others may have more widespread hair loss
Spaks Homeopathy Approach
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment focuses on:
Controlling the autoimmune response
Stimulating healthy hair regrowth
Preventing further hair fall
Improving overall immunity and vitality
Offering a safe, natural, and side-effect–free solution

Dandruff
Overview
Dandruff is one of the most common scalp conditions, affecting nearly 50% of people worldwide at some point in their lives, regardless of gender or ethnicity.
It is a scalp disorder characterized by flaking, itching, and irritation. Dead skin cells on the scalp clump together due to surface oil and debris, leading to visible white or yellowish flakes and sometimes excessive hair shedding.
Dandruff most often occurs between puberty and middle age, when sebaceous (oil) glands are most active. The severity can vary with the season—often worsening in winter due to dry air.
If left untreated, dandruff may progress to fungal scalp infections, worsen itching, and contribute to significant hair fall.
Symptoms
-
Persistent itchy scalp
-
White or yellowish flakes on scalp, shoulders, or clothes
-
Scaly facial skin (especially around eyebrows and nose)
-
Recurrent ear eczema or scaling behind ears
-
Oily scalp with dry flakes
-
Rash on eyebrows or beard area
-
Redness or irritation on scalp and face
Causes
-
Overgrowth of Malassezia fungus on the scalp
-
Excess oil (seborrhea) leading to buildup of skin cells
-
Poor scalp hygiene or irregular hair washing
-
Hormonal changes during puberty or stress
-
Sensitivity to hair care products (contact dermatitis)
-
Cold, dry weather that worsens skin dryness
Effects
-
Constant itching and irritation affecting daily comfort
-
Visible flakes causing embarrassment or low self-esteem
-
Worsening of seborrheic dermatitis (a chronic inflammatory condition)
-
Possible progression to fungal infections if untreated
-
Increased hair fall due to persistent scratching and scalp inflammation
Treatment
1. Home Remedies
-
Regular washing with mild or herbal shampoos
-
Natural options like coconut oil, aloe vera, neem, or tea tree oil to reduce fungal growth and soothe scalp
-
Balanced diet rich in zinc, B vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids
2. Medicated Shampoos
-
Zinc pyrithione shampoos (antifungal, antibacterial)
-
Ketoconazole shampoos (antifungal, effective against Malassezia)
-
Selenium sulfide or coal tar shampoos (slow down skin cell turnover)
-
Salicylic acid shampoos (help remove flakes and reduce scaling)
3. Medical Treatment
-
In resistant or severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe topical antifungals, corticosteroids, or oral medications

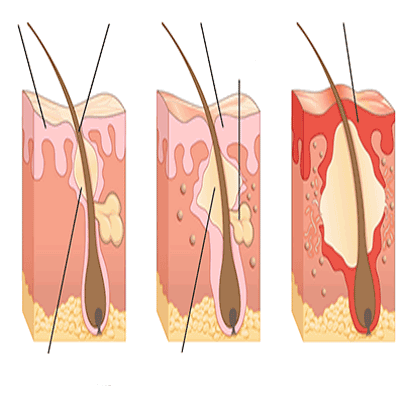
Folliculitis
Folliculitis – Overview (Spaks Homeopathy)
Folliculitis is a common skin condition in which the hair follicles become inflamed. It is most often caused by bacterial or fungal infection, but irritation, shaving, or blockage of hair follicles can also trigger it.
The condition usually starts as small red bumps or white-headed pimples around the hair follicles. In some cases, it may develop into pus-filled blisters, crusty sores, or large painful swellings. Although folliculitis is not life-threatening, it can be itchy, sore, and cosmetically embarrassing. Severe or recurring cases may lead to scarring and permanent hair loss.
Causes of Folliculitis
-
Bacterial infection (commonly Staphylococcus aureus)
-
Fungal or yeast infection
-
Shaving, waxing, or tight clothing causing irritation
-
Hot tubs or swimming pools with poorly maintained water (Hot tub folliculitis)
-
Ingrown hairs (common in beard area – Pseudofolliculitis barbae)
-
Use of oily creams or blocked sweat glands
Symptoms of Folliculitis
-
Clusters of small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles
-
Pus-filled blisters that may burst and form crusts
-
Itchy, burning, or painful skin
-
Swollen, tender lumps in severe cases
-
Large inflamed boils or carbuncles (deep follicle infections)
Effects / Complications
-
Chronic skin irritation and discomfort
-
Cosmetic concerns and loss of self-confidence
-
Spread of infection to nearby skin
-
Permanent hair loss in severe cases
-
Scarring of affected areas
Homeopathic Treatment for Folliculitis (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy works by controlling infection, reducing inflammation, and preventing recurrences without side effects. Some commonly prescribed remedies are:
-
Belladonna – for painful, red, and inflamed skin eruptions
-
Hepar Sulphuris – for pus-filled, tender boils that are very painful to touch
-
Sulphur – for chronic, recurring folliculitis with itching and burning
-
Graphites – for crusty, sticky eruptions with discharge
-
Silicea – for slow-healing boils and recurrent abscesses
Hair loss
Hair Loss? Don’t Worry – Regain Your Confidence with Homeopathy! ?
No harsh chemicals • 100% Safe • ? Natural & Effective
Causes of Hair Loss:
stress & Anxiety
Hormonal Imbalance (Thyroid, PCOD, Pregnancy)
Dandruff & Scalp Infections
Nutritional Deficiency
Genetics & Overuse of Chemicals
Effects if Ignored:
Thinning Hair | Baldness | Low Confidence
Homeopathy Benefits:
Stops Hair Fall Naturally
Boosts New Growth
Strengthens Roots & Scalp
Corrects Hormonal Imbalance
Top Remedies: Natrum Mur, Phosphorus, Lycopodium, Silicea, Thuja
Spaks Homeopathy – Your Hair, Skin & Confidence Partner!
+91 8700458818 | ?? info@spakshomeopathy.com
Don’t just cover hair loss, treat it from the root!
This version is short, punchy, and visually engaging, perfect for reels/captions.

Scarring Alopecia
Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia)
Overview
Scarring alopecia, also called cicatricial alopecia, is an inflammatory hair loss disorder that leads to permanent hair loss.
-
It occurs when hair follicles are destroyed and replaced by scar tissue.
-
Once destroyed, these follicles cannot regenerate hair.
-
In many cases, scarring alopecia begins as a non-scarring form of alopecia that slowly progresses to permanent hair loss.
Symptoms
-
Itching of the scalp
-
Burning sensation on the scalp
-
Pus or purulent discharge from scalp
-
Pain in affected areas
-
Patches of rough or scaly skin
-
Formation of blisters
-
Crusting over affected areas
Effects / Complications
-
Permanent bald patches on the scalp
-
Skin scarring at the affected sites
-
Emotional and psychological distress due to hair loss
-
Secondary infections in areas with pus or crusting
-
Potential spread of hair loss if inflammation is ongoing
Treatment
-
Medical Management
-
Anti-inflammatory medications: corticosteroids (topical, oral, or injectable) to reduce inflammation
-
Immunosuppressants: for autoimmune-related scarring alopecia (e.g., hydroxychloroquine, mycophenolate)
-
Antibiotics or antifungals: if secondary infection is present
-
-
Symptomatic Care
-
Soothing shampoos and scalp care to reduce itching or burning
-
Avoiding harsh hair treatments and heat styling
-
-
Surgical / Cosmetic Options
-
Hair transplant in stable, inactive areas (after inflammation subsides)
-
Scalp micropigmentation to camouflage bald patches
-
-
Early Intervention
-
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent further hair follicle destruction.
-
-

Traction alopecia
Traction Alopecia
Overview
Traction alopecia is hair loss caused by repeated pulling or tension on the hair, usually from tight hairstyles such as braids, ponytails, buns, or extensions.
-
Early stages: Hair loss is reversible; hair can regrow if the tension is relieved.
-
Advanced stages: Continuous strain damages hair follicles permanently, preventing regrowth.
Repeated tension on hair follicles can also lead to scalp irritation, redness, itching, and in some cases, infections or pus-filled sores.
Signs and Symptoms
-
Receding hairline around the forehead, temples, or nape of the neck
-
Small pimples or bumps at the base of braids or along the hairline
-
Redness, itching, or sores on the scalp
-
Widening of hair parting
-
Patches of thin, broken, or missing hair in areas under tension
-
Shiny, scarred scalp in advanced or long-term cases
Causes
-
Tight ponytails, buns, or braids
-
Hair extensions or weaves
-
Chemical treatments combined with tension
-
Repetitive use of headgear that pulls hair
Treatment / Management
-
Relieve Tension:
-
Stop tight hairstyles immediately
-
Avoid pulling, braiding, or chemical treatments that stress hair
-
-
Medical / Hair Treatments:
-
Topical or oral medications may reduce inflammation
-
Minoxidil or other hair-growth stimulants in early stages
-
Hair transplantation in severe, permanent cases
-
-
Supportive Care:
-
Gentle hair care routines
-
Avoid tight accessories or harsh chemical treatments
-
Treat infections promptly if present
-

Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania (Hair-Pulling Disorder)
Overview
Trichotillomania is a mental health disorder characterized by recurrent, irresistible urges to pull out hair from the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or other areas of the body.
-
Hair pulling often leaves patchy bald spots, causing significant emotional distress and social or occupational difficulties.
-
The severity varies: for some, it is mild and manageable, while for others, the urge is overwhelming.
-
Treatment options, including therapy and medications, can help reduce or stop hair pulling.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms often include:
-
Repeated hair pulling from the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or other body areas
-
Patchy bald spots, shortened hair, or noticeable thinning
-
Tension or anxiety before pulling, and a sense of pleasure or relief afterward
-
Preference for specific types of hair or patterns/rituals in hair pulling
-
Biting, chewing, or eating pulled hair (trichophagia)
-
Playing with pulled hair or rubbing it on lips or face
-
Repeated unsuccessful attempts to stop or reduce hair pulling
-
Significant distress or functional problems at work, school, or in social situations
Complications
-
Infections or sores from repeated pulling
-
Gastrointestinal issues if hair is ingested (trichobezoar)
-
Emotional problems such as anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem
-
Social withdrawal or embarrassment
Treatment / Management
-
Behavioral Therapy:
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), particularly Habit Reversal Training (HRT)
-
Helps identify triggers, replace pulling with alternative behaviors
-
-
Medications:
-
SSRIs or other psychiatric medications in some cases
-
-
Supportive Care:
-
Stress management, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques
-
Support groups or therapy for emotional support
-
