Bruxism
Bruxism – Spaks Homeopathy
Overview
Bruxism is a condition where you grind, clench, or gnash your teeth, either when awake (awake bruxism) or during sleep (sleep bruxism).
Sleep bruxism is classified as a sleep-related movement disorder. People who grind their teeth at night are more likely to have other sleep issues such as snoring or sleep apnea.
Mild bruxism may not require treatment. However, if severe and frequent, it can lead to jaw problems, headaches, broken teeth, and other complications.
Since sleep bruxism often goes unnoticed until damage occurs, it’s important to be aware of its signs and seek regular dental and medical attention.
Symptoms of Bruxism
-
Grinding or clenching of teeth (may be loud enough to disturb others)
-
Teeth that are flattened, chipped, fractured, or loose
-
Worn tooth enamel, exposing deeper layers
-
Increased tooth pain or sensitivity
-
Tight or tired jaw muscles, difficulty opening/closing the jaw
-
Jaw, neck, or face pain
-
Pain resembling an earache (without ear issues)
-
Dull headache starting from the temples
-
Damage to the inside of the cheek from chewing
-
Sleep disruption
Spaks Homeopathy Care:
Gentle, side-effect-free remedies help in relieving jaw tension, reducing headaches, protecting teeth, and improving sleep quality, ensuring better long-term oral and overall health.
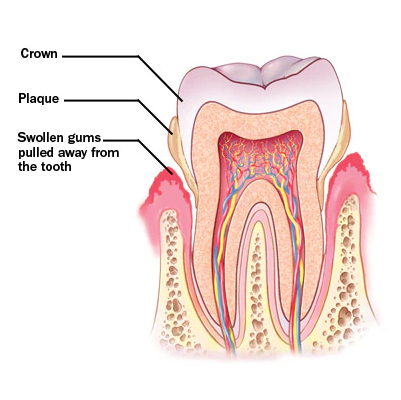
Dental Calculus
Overview
Dental calculus (tartar) is a hardened form of plaque that builds up on teeth.
When we eat foods rich in sugars and carbohydrates, bacteria in the mouth release acids that attack the teeth. This leads to plaque formation, a sticky film that coats teeth and gums.
Over time, plaque absorbs minerals from saliva and hardens into calculus (tartar). Unlike plaque, tartar is rough, hard, and firmly attached to teeth – and cannot be removed by simple brushing.
It is most commonly found:
-
On the outer surface of upper molars (near salivary ducts).
-
On the inner surface of lower front teeth.
Almost everyone develops some plaque, but once tartar forms, it requires professional dental cleaning.
Symptoms
-
Swollen or puffy gums
-
Red, dusky, or purplish gums
-
Tender gums (painful when touched)
-
Easy bleeding while brushing or flossing
-
Gum recession – teeth appear longer than normal
-
New gaps forming between teeth
-
Bad breath and metallic taste
Effects / Complications
If calculus is ignored, it may lead to:
-
Gingivitis (gum inflammation)
-
Periodontitis (advanced gum disease damaging bone)
-
Tooth mobility & loss
-
Persistent halitosis (bad breath)
-
Aesthetic issues – yellowish/brown deposits visible on teeth
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Spaks Homeopathy helps in reducing gum inflammation, controlling plaque formation, and strengthening teeth naturally:
-
Mercurius Solubilis – for swollen, bleeding gums with offensive odor.
-
Silicea – strengthens weak teeth, prevents recurrent gum infections.
-
Calcarea Fluorica – prevents tartar deposits and helps with receding gums.
-
Kreosotum – useful in decayed teeth with painful gums.
-
Plantago (Mother Tincture) – for toothache, gum tenderness, and bad breath.
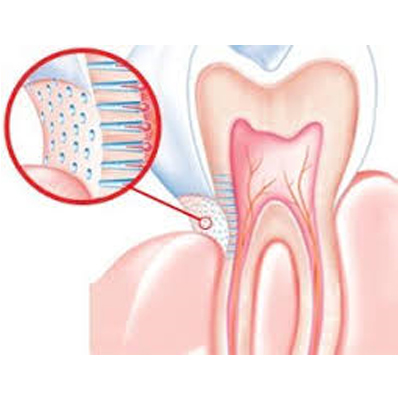
Dentin Hypersensitivity
Overview
Dentin hypersensitivity is a common oral condition marked by sharp, short-lasting pain in one or more teeth.
The discomfort occurs when exposed dentin reacts to external stimuli such as:
-
Thermal (hot/cold drinks or food)
-
Tactile (touch, brushing, dental instruments)
-
Evaporative (air exposure)
-
Chemical (acidic or sweet foods)
It affects both genders but is more common in females, typically between 20–40 years of age.
The most affected teeth are canines and premolars, especially on the buccal cervical region.
Because of its frequent occurrence, it is often referred to as the “common cold of dentistry” or the “toothbrush disease.”
Symptoms
-
Sharp, sudden tooth pain triggered by cold, hot, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
-
Discomfort when brushing teeth or touching the affected area.
-
Pain while inhaling cold air.
-
Localized pain that subsides once the stimulus is removed.
Effects / Complications
If ignored, dentin hypersensitivity may lead to:
-
Avoidance of proper brushing, causing plaque buildup.
-
Increased risk of cavities in the sensitive area.
-
Gum recession due to overbrushing or wrong brushing technique.
-
Impact on quality of life – difficulty in eating, drinking, or even speaking freely.
-
Progression to pulpitis (if sensitivity worsens).
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Homeopathy offers safe and effective remedies to reduce tooth sensitivity, strengthen dentin, and improve gum health:
-
Calcarea Fluorica – for enamel strengthening, cracks in teeth, and sensitivity.
-
Silicea – useful for weak, sensitive teeth prone to pain.
-
Plantago Major (Mother Tincture) – excellent remedy for toothache, sensitivity, and neuralgic pains.
-
Kreosotum – for sensitive teeth with decaying tendency.
-
Mercurius Solubilis – when pain is associated with swollen, tender gums and bad breath.
Alongside Spaks Homeopathy treatment, dentists advise:
-
Using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
-
Avoiding excessive acidic/sugary foods.
-
Practicing proper brushing techniques.
Dental Plaque
Overview
Dental plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that continuously forms on the teeth and along the gum line.
Plaque develops naturally due to the interaction of bacteria, saliva, and food particles in the mouth. If not removed regularly through brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar (calculus). This increases the risk of tooth decay, cavities, and gum disease.
Symptoms of Dental Plaque & Gum Disease
-
Teeth may feel fuzzy or rough when touched with the tongue.
-
In early stages, plaque is often invisible but can give a dull appearance to teeth.
-
In advanced stages, it may appear as a white, grayish, or yellowish coating on teeth.
-
If left untreated, it can progress to gum inflammation (gingivitis), bleeding gums, and bad breath.
Effects / Complications
If plaque is not managed properly, it can lead to:
-
Tooth decay and formation of cavities.
-
Gingivitis (red, swollen, bleeding gums).
-
Periodontitis, a severe gum infection that damages soft tissue and bone.
-
Tooth loss in advanced stages.
-
Persistent bad breath and oral infections.
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Spaks Homeopathy offers gentle, side-effect–free remedies that target the root cause of plaque buildup and gum disease:
-
Mercurius Solubilis – for swollen, bleeding gums with foul breath.
-
Kreosotum – for decayed teeth and sensitive gums.
-
Silicea – strengthens teeth and helps in recurrent gum infections.
-
Calcarea Fluorica – for tartar deposits and loosened teeth.
-
Plantago (Mother Tincture) – excellent for toothache, dental sensitivity, and reducing plaque.
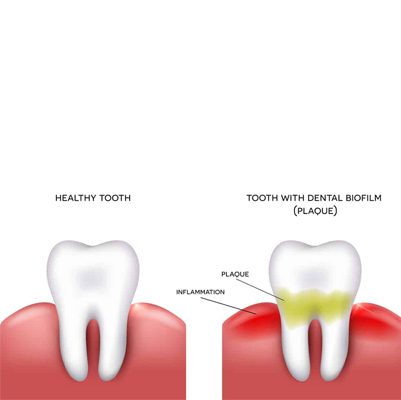
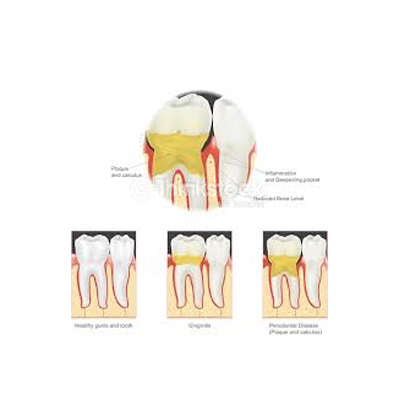
Gingivitis
Gingivitis – Overview (Spaks Homeopathy)
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that causes irritation, redness, and swelling (inflammation) of the gums. It usually occurs due to poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque (a sticky film of bacteria) to build up on the teeth.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis, a more serious condition that may lead to tooth loss and gum damage.
Causes of Gingivitis
-
Poor dental hygiene (irregular brushing or flossing)
-
Plaque and tartar buildup
-
Smoking or tobacco use
-
Vitamin C deficiency (Scurvy)
-
Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
-
Hormonal changes (pregnancy, puberty, menopause)
-
Diabetes and other systemic diseases
Symptoms of Gingivitis
-
Red, swollen, or tender gums
-
Bleeding while brushing or flossing
-
Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
-
Receding gums
-
Soft gums that hurt on touch
-
Metallic taste in the mouth
Effects / Complications if Untreated
-
Chronic gum infection
-
Gum recession and tooth loosening
-
Periodontitis (advanced gum disease)
-
Bone damage around teeth
-
Tooth loss
-
Increased risk of systemic issues (heart disease, diabetes complications)
Homeopathic Treatment for Gingivitis (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy provides a natural and gentle approach to treat gum inflammation, bleeding, and bad breath, while improving overall oral health. Remedies are selected based on individual symptoms:
-
Mercurius Solubilis – for swollen, spongy gums with excessive salivation and metallic taste
-
Kreosotum – for bleeding gums with offensive odor and decayed teeth
-
Silicea – for pus formation, gum abscess, and weak roots of teeth
-
Hepar Sulphuris – for painful, sensitive gums with tendency to abscess
-
Carbo Vegetabilis – for bleeding gums with foul breath and burning sensation
-
Phosphorus – for easily bleeding gums with tooth sensitivity
Note: Regular brushing, flossing, dental check-ups, and avoiding tobacco are essential along with homeopathic remedies.
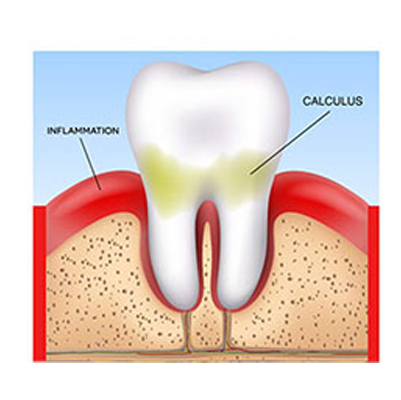
Gum
Overview
Periodontal disease (gum disease) is an infection of the tissues and bones that support your teeth.
It usually begins with plaque buildup on teeth due to improper brushing and flossing. When plaque hardens into tartar, bacteria grow beneath the gum line, leading to infection.
If untreated, it progresses from gingivitis (mild gum inflammation) to periodontitis (serious gum damage). In advanced cases, it may cause tooth loosening or even tooth loss.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
-
Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
-
Red, swollen, or tender gums
-
Gums that bleed easily (especially while brushing)
-
Pain while chewing
-
Loose or shaky teeth
-
Tooth sensitivity
-
Receding gums or teeth appearing longer
Effects of Untreated Gum Disease
-
Chronic gum pain and swelling
-
Gum recession leading to tooth exposure
-
Formation of pockets around teeth filled with pus
-
Loss of supporting bone structure
-
Loosening and eventual loss of teeth
-
Increased risk of systemic diseases (heart disease, diabetes complications, respiratory infections)
Homeopathic Treatment for Periodontal Disease
Homeopathy focuses on reducing infection, healing gums, and strengthening overall oral health. Commonly used remedies include:
-
Mercurius solubilis – for swollen, spongy gums with offensive breath and bleeding
-
Kreosotum – when gums are inflamed with decayed teeth and putrid odor
-
Silicea – for gum abscesses and slow-healing infections
-
Phosphorus – for bleeding gums with tooth sensitivity
-
Hepar sulphuris – for painful, infected gums with pus formation
Along with remedies, maintaining oral hygiene (brushing twice, flossing, and rinsing with salt water) is essential.
Hyperdontia
What is Hyperdontia?
Hyperdontia is a dental condition in which a person develops extra teeth in the mouth beyond the normal number. These additional teeth are called supernumerary teeth.
They can appear in the dental arches (the curved areas where teeth attach to the jaw).
-
Humans normally develop 20 primary (baby/deciduous) teeth and later 32 permanent (adult) teeth.
-
In hyperdontia, there may be extra primary or permanent teeth.
-
Extra primary teeth are less common, while extra permanent teeth are more frequently seen in adults.
Symptoms of Hyperdontia
-
Extra teeth often appear in adulthood.
-
More common in men than women.
-
Can occur in both the upper and lower jaw, though most often seen in the upper front teeth region (mesiodens).
-
Extra teeth are classified by shape and location:
By Shape
-
Supplemental – resembles the normal tooth next to it.
-
Tuberculate – barrel/tube-shaped.
-
Compound odontoma – cluster of small tooth-like structures.
-
Complex odontoma – disorganized mass of tooth tissue.
-
Conical (peg-shaped) – narrow at the top, wide at the base, cone-like.
By Location
-
Mesiodens – between two upper front teeth.
-
Paramolar – near molars.
-
Distomolar – behind molars (sometimes called “fourth molar”).
Effects of Hyperdontia
If untreated, extra teeth can cause:
-
Crowding of teeth
-
Misalignment or shifting of normal teeth
-
Delayed eruption of permanent teeth
-
Gaps or spacing problems
-
Difficulty chewing or speaking
-
Jaw pain or discomfort
-
Increased risk of cysts, infections, or gum issues
Treatment for Hyperdontia
Treatment depends on the number, type, and impact of extra teeth:
-
Observation – If extra teeth don’t cause crowding or other problems, no immediate treatment may be needed.
-
Extraction (removal) – Recommended if extra teeth cause misalignment, pain, or risk of complications.
-
Orthodontic treatment (braces or aligners) – To correct spacing, bite, or alignment after removal.
-
Surgical removal – For impacted or deeply embedded teeth.
Homeopathic Support (complementary, under guidance)
-
Calcarea phosphorica – for delayed or irregular tooth eruption.
-
Silicea – for strengthening teeth and preventing infections.
-
Calcarea fluorica – for dental crowding and abnormal tooth structure.
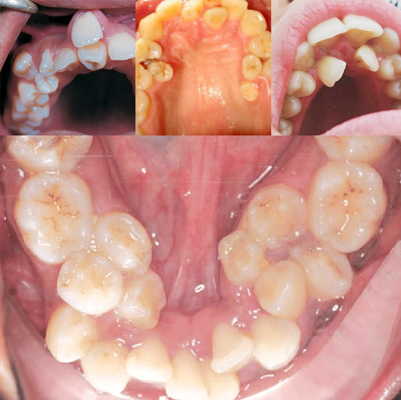
Periodontitis
Periodontitis
Overview
Periodontitis is a serious gum infection that damages both the soft tissue and the bone that supports your teeth. If untreated, it can cause tooth loosening or even tooth loss.
It is a common dental condition but is largely preventable. The most frequent cause is poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque — a sticky film of bacteria — to build up and harden on the teeth.
Good oral care habits, such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and having regular dental checkups, can significantly reduce the risk and improve treatment success.
Symptoms
Healthy gums are firm, pale pink, and fit snugly around the teeth. With periodontitis, symptoms may include:
-
Swollen or puffy gums
-
Bright red, dusky red, or purplish gums
-
Tender gums (pain when touched)
-
Gums that bleed easily (especially while brushing or flossing)
-
Gum recession (teeth appearing longer than usual)
-
New gaps or spaces developing between teeth
-
Pus between teeth and gums
-
Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
-
Loose or shifting teeth
-
Painful chewing
-
Change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
Effects
-
Progressive loss of gum tissue and supporting bone
-
Tooth instability and tooth loss
-
Chronic bad breath and discomfort
-
Increased risk of systemic health issues (linked to heart disease, diabetes, respiratory disease)
-
Negative impact on appearance, confidence, and nutrition
Treatment
Treatment focuses on controlling the infection, restoring gum health, and preventing further damage:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments:
-
Scaling and root planing – deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar below the gumline
-
Antibiotics – topical gels or oral antibiotics to control bacterial infection
2. Surgical Treatments (in advanced cases):
-
Flap surgery (pocket reduction surgery): gums are lifted back for deep cleaning and sutured to fit tightly around teeth
-
Bone grafts: replace lost bone and encourage regeneration
-
Soft tissue grafts: strengthen thin or receding gums
-
Guided tissue regeneration: stimulates bone regrowth around affected teeth
3. Home & Lifestyle Care:
-
Brush teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
-
Daily flossing to remove plaque between teeth
-
Use of antimicrobial mouth rinses if recommended
-
Quit smoking, as it increases risk and severity
-
Regular professional dental cleaning (every 6 months or more often if needed)