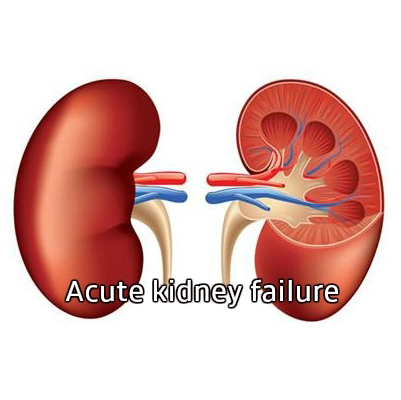
Acute kidney Failure
Acute Kidney Failure – An Overview
Acute Kidney Failure, also known as Acute Renal Disorder or Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), occurs when the kidneys suddenly lose their ability to filter waste products from the blood.
As a result, dangerous levels of waste and toxins build up in the body, disturbing the chemical balance of blood. This condition usually develops within a few days and is most common among people who are already hospitalized or critically ill.
Acute Kidney Failure can be life-threatening and requires urgent medical attention. However, with timely treatment, the condition can be reversible, and kidney function may return to normal or near-normal if the patient is otherwise healthy.
Symptoms of Acute Kidney Failure
-
Decreased urine output (though sometimes it remains normal)
-
Fluid retention, causing swelling in legs, ankles, or feet
-
Shortness of breath
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Nausea and confusion
-
Irregular heartbeat
-
Chest pain or pressure
-
Seizures or coma in severe cases
Spaks Homeopathy Approach:
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment aims to:
Support kidney function naturally
Improve waste filtration and urine flow
Reduce swelling and related symptoms
Boost vitality and overall health
Prevent further damage—without side effects
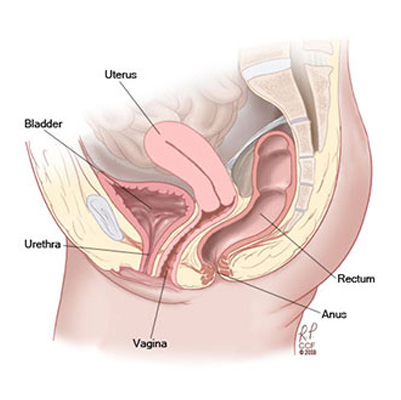
Cystocele
Overview
Cystocele, also called anterior prolapse or prolapsed bladder, occurs when the supportive tissue between a woman’s bladder and vaginal wall weakens. This causes the bladder to bulge into the vagina.
The condition is often the result of repeated straining on pelvic muscles—commonly during childbirth, chronic constipation, heavy lifting, or persistent coughing. It is also more common after menopause, when estrogen levels drop and pelvic tissues lose strength.
Mild cases may cause little or no discomfort, but moderate to severe cystocele can interfere with normal urination, sexual activity, and quality of life.
Symptoms
-
Sensation of fullness or pressure in the pelvis or vagina
-
Discomfort that worsens with coughing, straining, or lifting
-
Feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied after urination
-
Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
-
Pain or urinary leakage during intercourse
-
In severe cases, a visible bulge of tissue protruding from the vaginal opening
Effects
-
Increased risk of urinary incontinence
-
Higher chance of frequent bladder infections
-
Chronic pelvic pain or pressure
-
Interference with sexual health and intimacy
-
Severe untreated cases may affect daily mobility and confidence
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity:
1. Lifestyle & Self-care
-
Avoid heavy lifting and manage chronic coughing or constipation
-
Perform Kegel exercises to strengthen pelvic floor muscles
-
Maintain healthy body weight to reduce pressure on pelvic organs
2. Medical Options
-
Pessary device (inserted into the vagina to support the bladder)
-
Estrogen therapy (for postmenopausal women to strengthen tissues)
3. Surgical Treatment
-
Anterior colporrhaphy: surgical repair of the vaginal wall to restore bladder support
-
Surgery is usually considered for severe or recurrent cystocele that does not respond to conservative measures
With early diagnosis and proper treatment, most women experience significant relief from symptoms and regain normal function.
Diabetes Insipidus
Overview
Diabetes Insipidus (DI) is a rare disorder marked by excessive thirst (polydipsia) and the production of large volumes of dilute urine (polyuria).
It occurs due to a deficiency of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone – ADH) or the kidney’s inability to respond to it. Vasopressin normally regulates water balance in the body by controlling urine concentration.
Although the name sounds similar to diabetes mellitus, the two are unrelated. Diabetes mellitus is linked to blood sugar levels, whereas diabetes insipidus is a water-balance disorder.
There is currently no permanent cure, but proper treatment and management help control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Symptoms of Diabetes Insipidus
-
Extreme, unquenchable thirst (even after drinking water)
-
Excessive urination (polyuria)
-
Colourless urine instead of pale yellow
-
Waking multiple times at night to urinate (nocturia)
-
Bedwetting (especially in children)
-
Dry skin
-
Constipation
-
Weak muscles or fatigue
Effects / Complications
If untreated, Diabetes Insipidus can lead to:
-
Dehydration (due to constant water loss).
-
Electrolyte imbalance (sodium and potassium levels disturbed).
-
Low blood pressure & dizziness.
-
Kidney strain from continuous urine output.
-
Weakness, confusion, and irritability.
-
In severe cases, seizures or unconsciousness due to fluid imbalance.
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Homeopathy helps restore fluid balance, improves kidney function, and reduces excessive urination naturally without side effects. Common remedies include:
-
Phosphoric Acid – For excessive thirst, weakness, and frequent urination.
-
Apis Mellifica – Helps in cases with swelling, dryness, and fluid imbalance.
-
Natrium Muriaticum – For intense thirst and dryness with frequent urination.
-
Helonias Dioica – Useful in diabetes insipidus with kidney weakness.
-
Causticum – For bedwetting and weak bladder control.
-
Syzygium Jambolanum (supportive) – Helps balance fluid metabolism.
Diabetic nephropathy
Overview
Diabetic Kidney Disease (Diabetic Nephropathy) is a serious kidney-related complication that can occur in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Nearly 40% of people with diabetes may eventually develop some form of kidney disorder.
It occurs when high blood sugar and high blood pressure damage the kidney’s delicate filtering system over time, reducing its ability to remove waste and excess fluid from the body.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, keeping blood sugar and blood pressure under control, and starting early treatment are key to slowing down the disease and preventing complications.
Symptoms
In the early stages, there are usually no noticeable symptoms.
As the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
-
Worsening blood pressure control
-
Protein in the urine (first sign of kidney damage)
-
Swelling in feet, ankles, hands, or eyes (edema)
-
Increased urge to urinate
-
Lower requirement for insulin or diabetes medicines
-
Confusion or difficulty concentrating
-
Loss of appetite
-
Nausea and vomiting
Effects / Complications
If untreated, Diabetic Kidney Disease may lead to:
-
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
-
End-stage kidney failure (requiring dialysis or transplant)
-
Fluid retention → swelling in legs, high blood pressure, fluid in lungs
-
Electrolyte imbalance → muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat
-
Anemia (low red blood cells due to reduced kidney function)
-
Bone weakness due to altered calcium-phosphorus balance
-
Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases (heart attack, stroke)
Treatment with Spaks Homeopathy
Homeopathy aims to strengthen kidney function, control sugar levels, and reduce progression of kidney damage naturally, without side effects. Remedies are selected based on the patient’s constitution and symptoms.
? Key Remedies Used in Spaks Homeopathy:
-
Arsenicum Album – For swelling, fatigue, weakness, and burning thirst.
-
Phosphorus – For protein in urine, kidney inflammation, and debility.
-
Lycopodium – For digestive issues with kidney problems, swelling, and weakness.
-
Apis Mellifica – For edema, puffiness around eyes, and water retention.
-
Terebinthina – For blood in urine and early kidney degeneration.
-
Syzygium Jambolanum (supportive) – Helps regulate high blood sugar naturally.
Dysuria
Dysuria (Painful Urination)
Overview
Dysuria means pain, burning, or discomfort while urinating. It is commonly caused by urinary tract infections (UTIs) but can also occur due to problems in the bladder, urethra, or reproductive organs.
The most frequent cause is bladder infection (cystitis), especially in women aged 20–50. Infections usually develop when bacteria enter the urethra during sexual activity or from improper wiping (back to front), allowing them to reach the bladder.
Symptoms
1. Bladder Infection (Cystitis):
-
Frequent urination
-
Urgent need to urinate
-
Pain/pressure in lower abdomen
-
Cloudy, strong-smelling urine
-
Blood in urine
2. Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis):
-
Pain in upper back or sides
-
High fever, chills
-
Nausea, vomiting
-
Cloudy urine
-
Strong urge to urinate
3. Urethritis (Urethra Infection):
-
Burning while urinating
-
Urethral discharge
-
Redness/irritation at urethra opening
-
Vaginal discharge in women
4. Vaginitis (Vaginal Infection):
-
Vaginal pain, soreness, itching
-
Abnormal discharge or odor
-
Pain during intercourse
Effects of Dysuria
-
Recurrent urinary infections
-
Sleep disturbance due to frequent urination
-
Stress and anxiety from discomfort
-
Kidney damage if left untreated (in severe cases)
-
Reduced quality of life
Homeopathic Treatment (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy offers gentle, side-effect-free remedies that not only relieve burning and pain but also reduce the tendency for recurring infections. Treatment is based on individual symptoms.
Cantharis – For intense burning pain before, during, and after urination.
Apis Mellifica – When urine is scanty, with stinging pains and swelling.
Sarsaparilla – For severe burning at the close of urination.
Nux Vomica – Suited for patients with frequent urge but little urine, along with abdominal cramps.
Staphysagria – Effective when dysuria is linked to sexual activity or emotional stress.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis – Overview (Spaks Homeopathy)
Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the tiny filters in the kidneys called glomeruli. These glomeruli normally remove excess fluid, electrolytes, and waste products from the blood and pass them into the urine.
This condition may appear suddenly (acute) or develop gradually (chronic) over time. It can occur on its own or as a complication of other systemic diseases such as lupus, diabetes, or infections.
If left untreated, severe or prolonged inflammation can damage the kidneys and lead to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure.
Causes of Glomerulonephritis
-
Autoimmune diseases (Lupus, Goodpasture’s syndrome)
-
Infections (streptococcal throat/skin infections, hepatitis B & C)
-
Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels)
-
Diabetes-related kidney damage
-
High blood pressure
-
Genetic predisposition
Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
-
Cola or tea-colored urine (due to blood in urine)
-
Excessive protein in urine (proteinuria)
-
Swelling (edema) in face, hands, feet, and abdomen
-
High blood pressure
-
Reduced urine output
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Nausea, vomiting, or shortness of breath (in severe cases)
Effects / Complications if Untreated
-
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
-
Kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplant
-
Severe hypertension
-
Fluid overload (leading to lung swelling or heart strain)
-
Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases
Homeopathic Treatment for Glomerulonephritis (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy focuses on reducing inflammation, improving kidney function, and controlling associated symptoms such as swelling, high blood pressure, and protein loss. Some effective remedies are:
-
Apis Mellifica – for swelling (edema), puffiness around eyes, and scanty urine
-
Arsenicum Album – for burning urine, extreme weakness, and swelling of limbs
-
Cantharis – for painful, burning urination with blood in urine
-
Terebinthina – for smoky/cola-colored urine with kidney irritation
-
Mercurius Corrosivus – for painful, scanty urine with blood and protein loss
-
Digitalis – for kidney involvement with weak heart and fluid retention
Hematuria
Overview
The presence of blood in your urine (pee) is known as hematuria. It can signal a problem with your kidneys or another part of the urinary tract.
There are two types:
-
Gross Hematuria – Blood is visible in urine, making it appear pink, red, or brown.
-
Microscopic Hematuria – Blood is not visible to the naked eye and is detected only under a microscope during a urine test.
Although sometimes the cause may be harmless, hematuria can also indicate a serious medical condition, so it should never be ignored.
Symptoms
-
No symptoms (in many cases of microscopic hematuria)
-
Urine appearing pink, red, or cola-colored
-
Blood clots in urine, which may cause pain
-
Burning sensation or pain while urinating (in some cases)
-
Increased frequency or urgency of urination (if linked with infection)
Hematuria is a symptom, not a disease itself. Proper evaluation and timely treatment are essential to find and address the underlying cause.
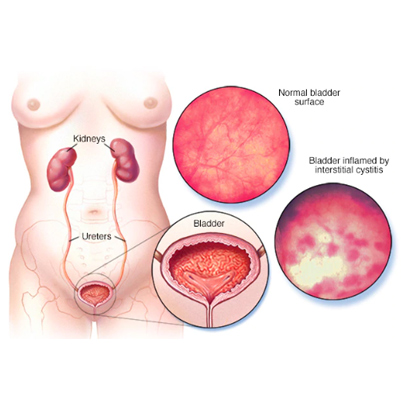
Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial Cystitis (IC) – Painful Bladder Syndrome
Overview
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also called painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic condition that causes bladder pressure, bladder pain, and sometimes pelvic pain. The intensity of pain may range from mild discomfort to severe, interfering with daily life.
Normally, the bladder stores urine and signals the brain through pelvic nerves when it is full. In IC, these signals get disrupted, making you feel the urge to urinate more frequently and with smaller volumes than usual.
This condition is more common in women and can have a long-term impact on quality of life. While there is no permanent cure, treatments and homeopathy may help relieve symptoms and improve bladder health.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary from person to person, but common signs include:
-
Pain in the pelvis or between the vagina and anus in women
-
Pain between the scrotum and anus (perineum) in men
-
Chronic pelvic pain
-
Increased urgency to urinate
-
Frequent urination, often in small amounts (sometimes up to 60 times a day)
-
Pain or discomfort when the bladder fills, with relief after urination
-
Pain during or after sexual intercourse
-
Symptoms that worsen with stress, exercise, or certain foods
Effects
-
Sleep disturbance due to frequent night urination
-
Constant discomfort affecting work and social life
-
Emotional stress, anxiety, and depression
-
Reduced sexual satisfaction due to painful intercourse
-
Risk of bladder wall scarring or reduced bladder capacity over time
Homeopathic Treatment
-
Cantharis – for severe burning pain during urination with frequent urges
-
Sarsaparilla – for painful urination, especially at the end, with bladder discomfort
-
Apis mellifica – for stinging, burning bladder pain with frequent, scanty urine
-
Borax – for frequent urination associated with pelvic pain and tenderness
-
Pulsatilla – for bladder pain and discomfort that worsens with stress or emotional strain