Nocturnal Enuresis
Bed-Wetting (Nocturnal Enuresis)
Overview
Bed-wetting — also called nighttime incontinence or nocturnal enuresis — is the involuntary passing of urine during sleep after the age when most children have achieved nighttime bladder control.
It is a common developmental stage for many children and is not a sign of failed toilet training. In most cases, children outgrow it naturally. Generally, bed-wetting before age 7 is not a concern, as bladder control is still developing.
By adolescence, bed-wetting becomes rare but can still occur, affecting about 4% of boys and 2% of girls, dropping further by age 18. For teenagers, persistent bed-wetting can cause emotional distress and social embarrassment.
If it continues, management with patience, reassurance, and supportive treatments is essential.
Symptoms
-
Wetting the bed at night (after age 5–7)
-
Occasional or frequent episodes of nighttime incontinence
-
Sometimes associated with urgency or heavy sleep
-
Normal urination patterns during the day (in most children)
Effects (Complications)
Although bed-wetting is usually harmless, it may lead to:
-
Emotional distress – embarrassment, guilt, or low self-esteem
-
Sleep disturbances – disrupted rest due to wet sheets and clothing
-
Social challenges – reluctance to attend sleepovers, school trips, or camps
-
Family stress – frustration for both child and parents
-
Skin irritation or rash – due to prolonged contact with wet clothes/bedding
Treatment
Lifestyle & Behavioral Approaches
-
Patience & reassurance – avoid punishing the child; emotional support is key
-
Bladder training – encourage holding urine for slightly longer during the day to improve bladder capacity
-
Fluid management – limit fluids 1–2 hours before bedtime, especially caffeinated drinks
-
Bedtime bathroom visit – ensure the child empties the bladder before sleep
-
Moisture alarms – devices that detect wetness and wake the child to use the toilet
Medical Options (if necessary)
-
Desmopressin (DDAVP) – reduces nighttime urine production
-
Anticholinergic medicines – for children with bladder overactivity
-
Imipramine – rarely used, but may be considered for resistant cases
Homeopathic Support (Complementary Care)
(May help reduce frequency of episodes, but should be guided by a qualified homeopath)
-
Causticum – for involuntary urination, especially during first sleep
-
Sepia – for bed-wetting in deep sleepers, often girls
-
Equisetum – for frequent nighttime urination with no pain
-
Sulphur – for chronic cases where the child is restless in sleep
-
Kreosotum – for children who wet the bed in the early part of sleep
Note: Most children outgrow bed-wetting naturally. Treatment is mainly about support, reassurance, and gradual training, with medical or homeopathic options considered only if the problem persists into later childhood or adolescence.

Overactive Bladder
Overactive Bladder (OAB)
Overview
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition that causes a sudden, frequent, and difficult-to-control urge to urinate. In some cases, this urge may lead to involuntary urine leakage (urge incontinence).
OAB can significantly affect daily activities, work, sleep, and social life, often leading to embarrassment, stress, or isolation. However, the condition is treatable. A proper evaluation can help identify underlying causes, and with behavioral changes, medications, or advanced therapies, most people find relief.
Symptoms
With an overactive bladder, you may:
-
Feel a sudden, strong urge to urinate that is difficult to control
-
Experience urge incontinence (involuntary urine leakage after the urge)
-
Urinate frequently, often 8 or more times in 24 hours
-
Wake up two or more times at night to urinate (nocturia)
Effects
-
Emotional impact: embarrassment, anxiety, social withdrawal, and reduced quality of life
-
Sleep disturbance due to frequent nighttime urination, causing fatigue and irritability
-
Increased risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) from incomplete bladder emptying (in some cases)
-
Can worsen depression or stress in people already dealing with chronic conditions
-
Limits participation in daily activities, travel, or exercise due to fear of leakage
Treatment
Treatment usually starts with lifestyle and behavioral strategies, progressing to medical or surgical options if needed:
1. Behavioral Strategies
-
Bladder training (scheduled bathroom visits, delaying urination gradually to increase bladder capacity)
-
Pelvic floor (Kegel) exercises to strengthen bladder control
-
Fluid management (reducing caffeine, alcohol, and excessive fluid intake)
-
Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce bladder pressure
2. Medications
-
Anticholinergics or beta-3 agonists to relax bladder muscles and reduce urgency
-
Vaginal estrogen therapy (for postmenopausal women, when appropriate)
3. Medical Procedures (for severe or resistant cases)
-
Botox injections into the bladder muscle to reduce contractions
-
Nerve stimulation therapy (neuromodulation) to regulate bladder activity
-
Surgery (rare, last resort) to increase bladder capacity
4. Supportive Care
-
Absorbent pads or protective undergarments if needed
-
Counseling or support groups to cope with emotional effects
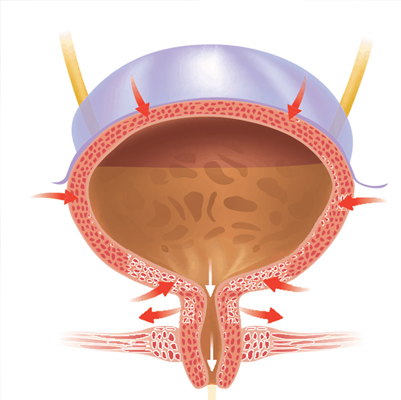
Polycystic Kidney
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
Overview
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder in which clusters of fluid-filled cysts develop in the kidneys. Over time, these cysts can cause the kidneys to enlarge and lose function.
The cysts are noncancerous and can vary in size, sometimes growing very large. Having many or large cysts may damage kidney tissue, leading to complications. PKD can also cause cysts in other organs, such as the liver.
PKD severity varies widely, and while it cannot be fully cured, lifestyle changes and treatments can help reduce kidney damage and manage complications like high blood pressure and kidney failure.
Symptoms
Polycystic kidney disease symptoms may include:
-
High blood pressure
-
Back or side pain
-
Headache
-
A feeling of fullness in the abdomen
-
Enlarged abdomen due to kidney enlargement
-
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
-
Urinary tract infections or kidney stones in some cases
Effects
-
Progressive kidney damage, potentially leading to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure
-
High blood pressure, increasing risk of heart disease or stroke
-
Abdominal discomfort or pain from enlarged kidneys
-
Risk of urinary tract infections and kidney stones
-
Complications in other organs, such as liver cysts
-
Reduced quality of life due to pain, fatigue, and frequent medical care
Treatment
While there is no cure for PKD, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression:
1. Lifestyle Measures:
-
Blood pressure control through diet, exercise, and medications
-
Low-salt diet to reduce fluid retention
-
Staying hydrated to prevent kidney stones and infections
-
Avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy weight
2. Medications:
-
Blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors or ARBs)
-
Pain relievers for back or abdominal pain (avoid nephrotoxic drugs)
-
Antibiotics for urinary tract infections
3. Procedures and Advanced Treatments:
-
Drainage of large cysts if causing severe pain or obstruction
-
Dialysis for kidney failure
-
Kidney transplantation in advanced disease
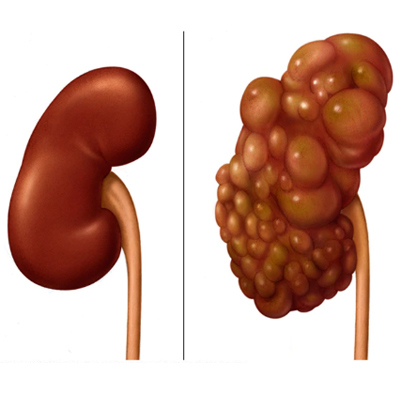
Prostatitis
Prostatitis
Overview
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system, a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine and semen exit the body. Its main function is to produce seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm.
Prostatitis is the swelling and inflammation of the prostate gland. It can affect men of all ages, though it is more common in men 50 or younger. Causes vary and can include bacterial infection, but in many cases, the exact cause is unknown.
When prostatitis is caused by bacteria, it can usually be effectively treated with antibiotics.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of prostatitis include:
-
Painful, difficult, or frequent urination
-
Blood in the urine
-
Groin, rectal, abdominal, or lower back pain
-
Fever and chills
-
Malaise and body aches
-
Urethral discharge
-
Painful ejaculation or sexual dysfunction
Effects
-
Chronic pelvic pain affecting quality of life
-
Urinary complications, such as difficulty or urgency in urination
-
Sexual dysfunction, including painful ejaculation or erectile issues
-
Recurrent urinary tract infections
-
Emotional distress, fatigue, and sleep disturbances due to chronic pain
Treatment
1. Medications:
-
Antibiotics (for bacterial prostatitis)
-
Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling
-
Alpha-blockers to relax bladder neck muscles and improve urine flow
-
Pain relievers for discomfort
2. Lifestyle Measures:
-
Frequent urination to prevent urine stagnation
-
Warm baths or sitz baths to relieve pelvic discomfort
-
Avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods that can irritate the bladder
-
Stress management and regular exercise to improve overall well-being
3. Procedures (for chronic or severe cases):
-
Prostate massage or physical therapy to relieve chronic pelvic pain
-
Surgical intervention in rare cases where obstruction or abscess occurs
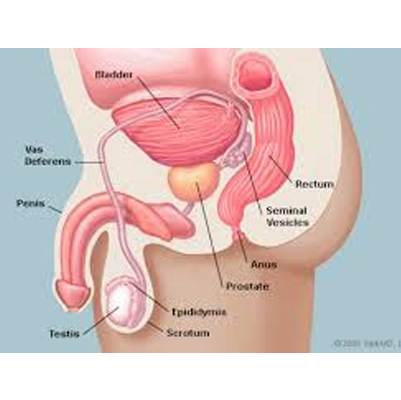
Pyelonephritis
Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis)
Overview
A kidney infection, also called pyelonephritis, is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that typically starts in the urethra or bladder and spreads to one or both kidneys.
Kidney infections require prompt medical attention. If untreated, they can permanently damage the kidneys or allow bacteria to spread to the bloodstream, causing a life-threatening infection (sepsis). Treatment usually involves antibiotics, and severe cases may require hospitalization.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a kidney infection include:
-
Fever and chills
-
Back, side (flank), or groin pain
-
Abdominal pain
-
Frequent urination
-
Strong, persistent urge to urinate
-
Burning sensation or pain while urinating
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Pus or blood in urine (hematuria)
-
Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
Effects
-
Permanent kidney damage, including scarring and decreased kidney function
-
Sepsis, a potentially life-threatening bloodstream infection
-
High blood pressure (hypertension) due to impaired kidney function
-
Recurrent kidney infections if the urinary tract is affected
-
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) in severe or untreated cases
-
General fatigue and reduced quality of life from prolonged illness
Treatment
1. Medications:
-
Antibiotics are the primary treatment, often starting with intravenous antibiotics for severe infections
-
Pain relievers to manage discomfort or flank pain
-
Antipyretics to control fever
2. Hospitalization:
-
Needed in cases of severe infection, dehydration, or sepsis
-
Intravenous fluids and antibiotics may be administered
3. Home Care and Lifestyle Measures:
-
Drink plenty of fluids to flush bacteria from the urinary tract
-
Rest to help the body recover
-
Avoid irritants like caffeine or alcohol during infection
-
Follow-up urine tests to ensure the infection is fully cleared
4. Prevention:
-
Proper hygiene, urinating after sexual activity
-
Treating underlying urinary tract abnormalities
-
Prompt treatment of bladder infections to prevent spread to kidneys
Pyuria
Pyuria
Overview
Pyuria is a urinary condition characterized by an elevated number of white blood cells (WBCs) in the urine, usually defined as at least 10 WBCs per cubic millimeter (mm³) of centrifuged urine.
This condition often causes the urine to appear cloudy or pus-like. Pyuria commonly occurs as a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI). In rare cases, it may indicate a complicated UTI or sepsis.
Sterile pyuria refers to pyuria without detectable bacteria in the urine. This can be due to non-detected bacteria, viral infections, other pathogens, or underlying medical conditions.
Symptoms
Symptoms of pyuria may vary and sometimes occur without other signs. They include:
-
Cloudy or pus-like urine
-
Blood in urine (hematuria)
-
Foul-smelling urine
-
Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
-
Fever
-
Abnormal discharge
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Shortness of breath in severe or systemic cases
Effects
-
Kidney damage if underlying infection is untreated
-
Sepsis, in severe cases of complicated pyuria
-
Recurrent UTIs leading to chronic urinary tract problems
-
Discomfort and reduced quality of life due to frequent urination or pain
-
Underlying disease complications if sterile pyuria is associated with autoimmune or inflammatory disorders
Treatment
1. Treat the Underlying Cause:
-
Bacterial infections: antibiotics based on urine culture results
-
Viral or non-bacterial causes: supportive care and monitoring
-
Underlying medical conditions: specific treatment depending on the cause
2. Symptom Relief:
-
Pain relievers for pelvic or abdominal discomfort
-
Hydration: drinking plenty of water to flush the urinary tract
3. Monitoring and Follow-Up:
-
Repeat urine tests to ensure resolution
-
Follow-up with a doctor if symptoms persist or worsen
4. Prevention (for recurrent cases):
-
Good urinary hygiene
-
Prompt treatment of UTIs
-
Avoiding irritants like caffeine or alcohol during infection

Renal tubular
Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA)
Overview
Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA) is a disorder in which the kidneys fail to properly excrete hydrogen ions, reabsorb bicarbonate, or produce aldosterone normally, leading to chronic metabolic acidosis.
This condition is often associated with electrolyte imbalances, including:
-
Hyperchloremia (excess chloride in blood)
-
Abnormal potassium and calcium levels
Chronic RTA results from damage to the renal tubules, and if left untreated, it can progress to chronic kidney disease and other serious complications.
Without proper treatment, RTA can affect growth in children, cause kidney stones, fatigue, muscle weakness, and over time may lead to bone disease, kidney failure, and heart problems.
Symptoms
RTA is often asymptomatic, especially in mild cases. Severe electrolyte imbalances, although rare, can be life-threatening. Common signs and symptoms include:
-
Nephrolithiasis (kidney stones)
-
Nephrocalcinosis (calcium deposits in the kidneys)
-
Electrolyte imbalances (low potassium or abnormal chloride levels)
-
Extracellular fluid volume depletion
-
Muscle weakness
-
Hyporeflexia (reduced reflexes)
-
Paralysis in severe cases
-
Bone pain in adults
-
Rickets in children (softening of bones)
-
Cardiac arrhythmias
Effects
-
Chronic kidney damage and potential kidney failure
-
Delayed growth and skeletal deformities in children
-
Bone disease due to prolonged acidosis
-
Muscle weakness and fatigue, affecting daily activities
-
Increased risk of kidney stones and nephrocalcinosis
-
Heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias) due to electrolyte imbalances
Treatment
1. Correcting Acidosis:
-
Alkali therapy (sodium bicarbonate or potassium citrate) to neutralize blood acidity
-
Potassium supplementation if hypokalemia is present
2. Managing Electrolyte Imbalances:
-
Careful monitoring of potassium, calcium, and chloride levels
-
Adjustments to diet or medications to prevent complications
3. Addressing Complications:
-
Kidney stones may require medications or procedures to remove them
-
Bone health can be supported with vitamin D and calcium supplementation
-
Cardiac monitoring in severe electrolyte disturbances
4. Long-Term Care:
-
Regular kidney function monitoring
-
Early intervention in children to ensure normal growth and bone development
-
Treatment of any underlying condition causing secondary RTA
Spermatorrhea
Spermatorrhea
Overview
Spermatorrhea is a condition of the male reproductive system characterized by the involuntary discharge of semen without sexual activity, orgasm, or erection.
-
It is commonly referred to as nightfall when it occurs during sleep.
-
The condition may be related to physical, psychological, or lifestyle factors, including excessive sexual activity, stress, or weakness in reproductive organs.
Symptoms
-
Pain or discomfort in the affected testicle
-
Heaviness in the testicle, sometimes with a spermatocele (fluid-filled sac)
-
Fullness behind or above the testicle
-
Weakness or fatigue
-
Yin deficiency (in traditional medicine terms)
-
Insomnia
-
Diarrhea
-
Enuresis (involuntary urination)
-
Premature ejaculation
-
Heart palpitations
Effects / Complications
-
Reduced sexual stamina and performance
-
Fatigue and weakness due to repeated loss of seminal fluid
-
Emotional stress, anxiety, or depression
-
Sleep disturbances from nightfall
-
Impact on reproductive health if underlying causes are untreated
Treatment
1. Lifestyle Modifications
-
Avoid excessive sexual activity or masturbation
-
Maintain healthy diet and hydration
-
Regular exercise and stress management
-
Proper sleep hygiene
2. Medical Treatment
-
Homeopathic or herbal remedies may be used to strengthen reproductive organs
-
Medications may be prescribed for associated conditions like insomnia or anxiety
-
Treat underlying urinary or endocrine issues if present
3. Psychological Support
-
Counseling for stress, anxiety, or sexual performance concerns
-
Relaxation techniques and mental health support
4. Preventive Measures
-
Balanced lifestyle with adequate rest
-
Avoiding stimulant intake (caffeine, alcohol, or nicotine)
-
Routine medical checkups to monitor reproductive health
