Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) – An Overview
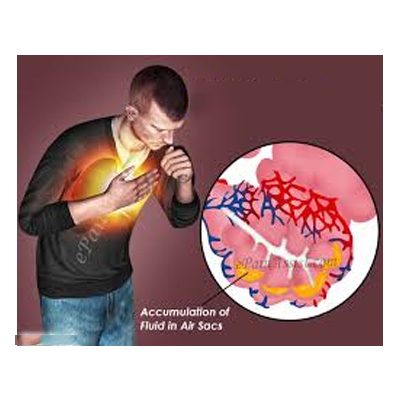
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a serious lung condition that occurs when fluid builds up in the tiny air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs.
This fluid prevents the lungs from filling with enough air, which means less oxygen reaches the bloodstream. As a result, the body’s organs are deprived of the oxygen they need to function properly.
ARDS usually develops in people who are already critically ill or have suffered major injuries or infections. The condition can progress quickly and requires urgent care.
The most prominent symptom is severe shortness of breath, which typically appears within a few hours to a few days after the underlying illness or injury.
Symptoms of ARDS
-
Severe shortness of breath
-
Labored and unusually rapid breathing
-
Low blood pressure
-
Confusion and extreme fatigue
Spaks Homeopathy Approach:
In ARDS, emergency medical support is primary. Alongside, Homeopathy can play a supportive role by:
Strengthening lung function
Reducing breathlessness and fatigue
Supporting immunity to fight infections
Improving overall recovery and vitality
Airway Obstruction
Airway Obstruction – An Overview
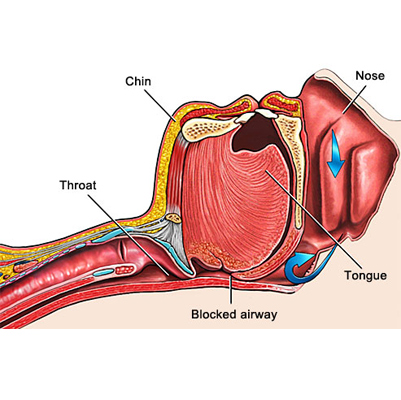
Airway Obstruction, also called Foreign Body Airway Obstruction, occurs when a small object gets stuck in a child’s throat or upper airway, making it hard for them to breathe.
Since children have smaller airways, even a tiny piece of food, a coin, marble, or toy part can cause blockage. In some cases, household items like plastic bags or cords may also lead to suffocation.
Every year, nearly 5,000 children under the age of 14 are treated in emergency rooms for airway obstruction, with most cases seen in children under 4 years old.
Symptoms of Airway Obstruction in Children
-
Choking or gagging
-
Sudden, forceful coughing
-
Vomiting during the episode
-
Noisy breathing or wheezing
-
Struggling or labored breathing
-
Skin or lips turning blue (cyanosis)
Spaks Homeopathy Approach
Airway obstruction is always a medical emergency requiring immediate first aid and hospital care. Once emergency care is given, Homeopathy helps in:
Supporting recovery after choking incidents
Reducing airway irritation and swelling
Strengthening the respiratory system
Preventing recurrence of breathing difficulties
Asthma attack
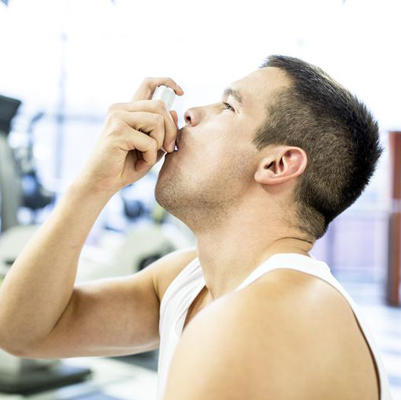
Asthma – An Overview
Asthma is a long-term respiratory condition in which the airways of the lungs become inflamed and narrowed, leading to difficulty in breathing. The muscles around the airways contract and mucus production increases, causing symptoms such as cough, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Asthma symptoms are usually intermittent and may worsen at night, early morning, or during physical activity.
Common Triggers
Asthma can be triggered by:
-
Viral infections (like cold & flu)
-
Dust, smoke, and strong fumes
-
Weather changes
-
Grass and tree pollen
-
Animal fur and feathers
-
Dust mites
-
Strong soaps, perfumes, or cleaning agents
-
Stress and certain foods
These triggers vary from person to person.
Diagnosis & Treatment
Asthma is often diagnosed with lung function tests, supported by blood tests and allergy testing.
Conventional treatment usually includes inhalers (beta-2 agonists & corticosteroids).
Lifestyle management also plays a major role – avoiding triggers, maintaining a healthy diet, and staying stress-free can significantly reduce attacks. In severe cases, asthma may lead to status asthmaticus, a life-threatening condition that requires hospitalization.
Symptoms of Asthma
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest tightness or pain
-
Coughing, especially at night or early morning
-
Wheezing (a whistling sound when breathing, common in children)
-
Trouble sleeping due to coughing or breathlessness
-
Recurrent coughing or wheezing worsened by cold or viral infections

Atelectasis
Atelectasis – Spaks Homeopathy Overview
The lungs are vital organs that supply oxygen to every part of the body. Atelectasis is a condition in which one or more areas of the lung collapse and cannot properly fill with air.
Normally, when we breathe in, the air travels into tiny air sacs (alveoli) inside the lungs, where oxygen passes into the blood to nourish the body. In atelectasis, these air sacs become deflated or blocked, reducing the flow of oxygen to the blood. If a large portion of the lung is affected, it can lead to serious breathing difficulties.
This condition often occurs after surgery but can also be linked to other lung problems. While mild cases may not be life-threatening, severe cases require timely treatment.
Signs & Symptoms of Atelectasis
-
Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
-
Rapid heartbeat
-
Persistent coughing
-
Chest discomfort or pain
-
Bluish skin or lips (due to lack of oxygen)
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment is aimed at:
Supporting natural lung function
Improving oxygen intake
Reducing discomfort and breathing issues
Promoting faster recovery without side effects
With gentle and effective remedies, Spaks Homeopathy helps restore healthy lung function and supports overall well-being.
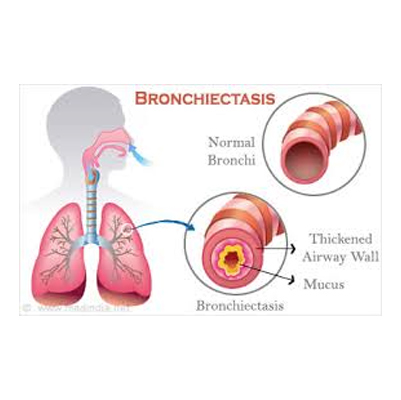
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis – Spaks Homeopathy
What is Bronchiectasis?
Bronchiectasis is a long-term lung condition in which the bronchial tubes (airways) become permanently damaged, widened, and thickened.
Because of this damage, mucus and bacteria can easily collect inside the lungs, leading to repeated infections and blockages in the airways.
Although there is no permanent cure for bronchiectasis, the condition is manageable. With proper treatment, many people are able to live a normal and active life. Quick treatment of flare-ups is essential to maintain proper airflow and prevent further lung damage.
Symptoms of Bronchiectasis
-
Persistent daily cough
-
Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
-
Abnormal chest sounds or wheezing while breathing
-
Shortness of breath
-
Chest pain
-
Coughing up large amounts of thick mucus every day
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Fatigue or constant tiredness
-
Clubbing of nails (change in shape of fingernails or toenails)
-
Frequent respiratory infections
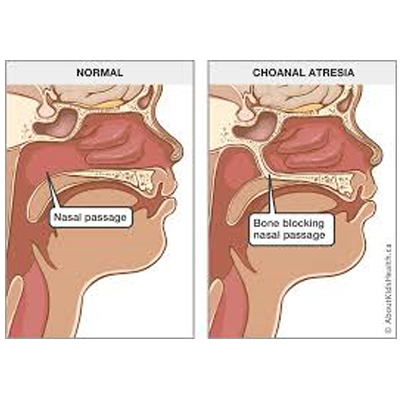
Choanal Atresia
What is Choanal Atresia?
Choanal atresia is a congenital condition (present at birth) in which the back of a baby’s nasal passage is blocked, making breathing difficult.
It is sometimes associated with other birth defects such as Treacher Collins syndrome or CHARGE syndrome.
-
Unilateral choanal atresia (one side blocked) is more common. Babies can manage by breathing through the open nasal passage.
-
Bilateral choanal atresia (both sides blocked) is more serious and dangerous because newborns rely mainly on nose breathing for the first 4–6 weeks of life.
Types of Choanal Atresia
-
Bilateral Choanal Atresia – Blocks both nasal passages; this is life-threatening without immediate medical help.
-
Unilateral Choanal Atresia – Blocks only one nasal passage, most often the right side.
Signs and Symptoms
-
Severe breathing difficulty at birth (bilateral cases)
-
Noisy breathing
-
Thick nasal discharge from one side (unilateral)
-
Child cannot breathe properly while feeding (leading to choking or distress)
Effects of Choanal Atresia
-
Poor feeding and weight loss due to breathing difficulty
-
Restless sleep and irritability
-
Increased risk of recurrent chest infections
-
Delayed development due to lack of proper oxygenation
-
Emotional stress for parents due to repeated breathing issues in the child
Homeopathy Treatment – Spaks Approach
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment for choanal atresia is focused on:
-
Improving breathing ability and reducing nasal blockage naturally
-
Strengthening immunity to reduce recurrent infections
-
Supporting overall growth and development of the baby
-
Gentle constitutional remedies that address congenital tendencies and improve vitality
-
Safe and side-effect-free medicines suitable for infants and children
Commonly used remedies (based on case history and symptoms):
-
Calcarea Carb – For children with recurrent nasal obstruction and slow development
-
Silicea – To reduce thick nasal discharge and boost immunity
-
Sambucus Nigra – For blocked nose and difficulty breathing during sleep
-
Baryta Carb – For delayed growth and frequent respiratory infections
At Spaks, each prescription is individualized after studying the baby’s symptoms, constitution, and family history. The goal is long-term relief, improved breathing, and better overall health.
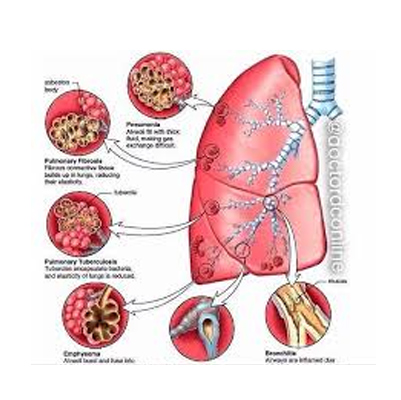
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Overview – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that makes it difficult to breathe. The two most common forms are:
-
Emphysema – gradual destruction of air sacs in the lungs, reducing airflow.
-
Chronic Bronchitis – inflammation and narrowing of the bronchial tubes, leading to excess mucus buildup.
The leading cause of COPD is tobacco smoking, though long-term exposure to dust, fumes, and chemical irritants also contributes. COPD develops slowly over years and often becomes noticeable in middle or older age.
Symptoms of COPD
-
Shortness of breath, especially during activity
-
Persistent chesty cough with phlegm (often mistaken as “smoker’s cough”)
-
Wheezing and chest tightness
-
Frequent chest infections
-
Fatigue and low stamina
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Swollen ankles or feet due to fluid retention (oedema)
Effects if Untreated
-
Progressive lung damage leading to respiratory failure
-
Reduced oxygen supply to body tissues
-
Pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in lung arteries)
-
Right-sided heart failure (cor pulmonale)
-
Severe disability and dependency on oxygen support
-
Decreased life expectancy and poor quality of life
Spaks Homeopathy Treatment
At Spaks Homeopathy, treatment for COPD focuses on slowing progression, easing breathing, strengthening immunity, and reducing complications.
Commonly Used Remedies (selected after case analysis):
-
Antimonium Tartaricum – For excessive mucus with rattling cough and breathlessness.
-
Arsenicum Album – For wheezing, anxiety, and difficulty in breathing, especially at night.
-
Bryonia Alba – For dry, painful cough with chest tightness.
-
Ipecacuanha – For constant wheezing with difficulty expelling phlegm.
-
Phosphorus – For weakness, chest infections, and recurrent respiratory issues.
-
Sulphur – For chronic bronchitis with persistent cough and irritation.
Why Choose Spaks Homeopathy?
-
Works on the root cause – not just symptom suppression.
-
Reduces frequency of chest infections and hospital visits.
-
Helps in better lung function and improved energy levels.
-
Safe, natural, and side-effect free treatment.
-
Customized prescriptions according to individual history.
Address: E-38, Budh Vihar, Badarpur, New Delhi – 110044
Email: info@spakshomeopathy.com
Phone: +91 8700458818
.jpg)
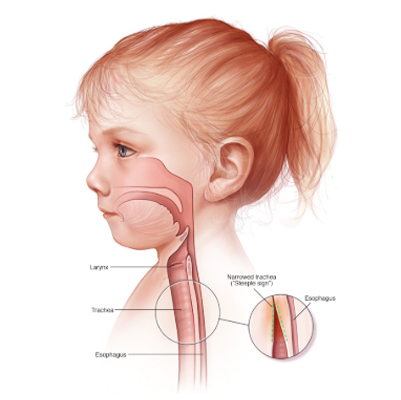
Croup
Overview
Croup is caused by an acute viral infection of the upper respiratory tract. It is also called laryngotracheobronchitis since it affects the larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), and bronchi (airways).
The infection leads to inflammation, swelling, and increased mucus production in the airways, which results in airflow obstruction and the characteristic “barking cough.”
Croup is most common in children between 6 months to 3 years, though it can occur at any age. Most cases are mild and resolve on their own, but in some cases, hospitalization may be required due to severe breathing difficulties.
It continues to be one of the most frequent causes of respiratory distress in young children.
Symptoms of Croup
-
Cold and cough (often starting like a common cold)
-
Barking cough (resembles a seal’s bark, worse at night)
-
Hoarseness of voice
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Stridor (high-pitched, noisy breathing, especially on inhalation)
-
Fever (mild to moderate)
-
Restlessness and irritability
-
In severe cases: rapid breathing, bluish lips/skin (cyanosis), fatigue
When to Seek Medical Help
-
Persistent stridor at rest
-
Difficulty in breathing or swallowing
-
Drooling, inability to speak or cry
-
High fever with worsening cough
-
Signs of cyanosis (bluish skin/lips)