Temporomandibular
TMJ Disorder (Temporomandibular Joint Disorder)
Overview
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a hinge connecting your jawbone to your skull, located on each side of the jaw. TMJ disorders, a type of temporomandibular disorder (TMD), affect this joint and the muscles controlling jaw movement.
The exact cause of TMJ disorders is often multifactorial, including:
-
Genetics
-
Arthritis
-
Jaw injury
-
Jaw clenching or teeth grinding (bruxism)
Most cases are temporary and can improve with self-care or medical treatments. Surgery is a last resort, reserved for severe cases.
Symptoms
-
Pain or tenderness in the jaw
-
Pain in one or both TMJ joints
-
Aching pain around the ear
-
Difficulty chewing or pain while chewing
-
Facial pain
-
Locking of the jaw, making it difficult to open or close the mouth
Effects / Complications
If untreated or persistent, TMJ disorders may cause:
-
Chronic jaw pain
-
Difficulty eating or speaking
-
Headaches or migraines
-
Earaches or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
-
Sleep disturbances due to pain or teeth grinding
Treatment / Management
1. Self-Care & Lifestyle:
-
Apply ice or heat to the affected area
-
Eat soft foods to reduce jaw strain
-
Avoid extreme jaw movements (e.g., wide yawning, chewing gum)
-
Stress management to reduce teeth clenching
2. Medical Treatment:
-
Pain relievers: NSAIDs like ibuprofen or acetaminophen
-
Muscle relaxants for jaw muscle spasms
-
Dental splints or mouthguards to prevent teeth grinding
-
Physical therapy for jaw exercises and posture improvement
3. Surgical Treatment (if conservative measures fail):
-
Arthrocentesis: flushing the joint
-
Arthroscopy: minimally invasive surgery
-
Open-joint surgery: for severe structural issues
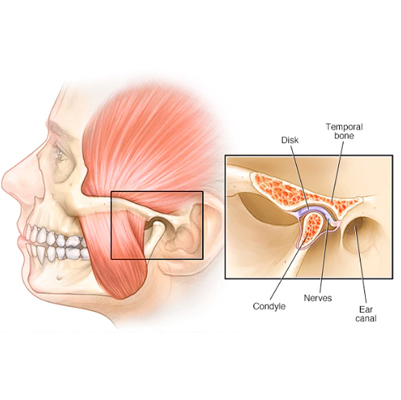
Tooth Worm
Tooth Worm (Tooth Decay / Tooth Infection)
Overview
The idea of a "tooth worm" is an erroneous theory—toothache or tooth infection is not caused by worms. In reality, dental problems arise from:
-
Bacterial buildup
-
Poor dental hygiene
-
Frequent snacking on sugary or starchy foods
These factors contribute to the formation of cavities and tartar on the teeth, which appear as small holes or worn areas. If untreated, cavities can progress to tooth decay, severe infections, or even tooth loss. Tooth decay can occur in individuals of all ages, from infants to adults.
Stages of Tooth Decay:
-
Initial Stage:
-
Bacteria accumulate on the tooth’s enamel (outer layer)
-
Plaque formation occurs, often due to starchy or sugary foods left on the teeth
-
Bacteria feed on these residues, causing enamel breakdown
-
-
Progression:
-
Plaque hardens into tartar
-
Cavities deepen, affecting dentin and potentially the tooth pulp
-
Infection can develop if bacteria reach the tooth nerve
-
Symptoms of Tooth Decay / Infection
-
Persistent bad breath
-
Red, swollen, or tender gums
-
Bleeding gums
-
Painful chewing
-
Loose teeth
-
Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods
-
Receding gums or teeth that appear longer
Treatment / Management
-
Professional Dental Care:
-
Fillings for cavities
-
Root canal treatment for infections reaching the pulp
-
Tooth extraction in severe cases
-
-
Preventive Measures:
-
Brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
-
Flossing daily
-
Limiting sugary and starchy foods
-
Regular dental checkups
-
-
Home Remedies / Supportive Care:
-
Rinsing with saltwater for minor gum inflammation
-
Using antibacterial mouthwash
-
Pain relief with OTC analgesics
-
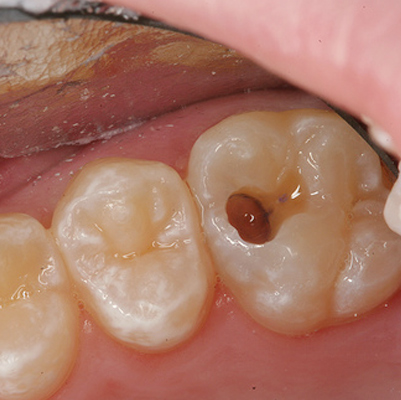
Toothache
Toothache
Overview
A toothache is pain felt in or around a tooth, caused by:
-
Tooth decay or cavities
-
Dental infection
-
Earache or sinus infection
-
Injury to the jaw joint (TMJ)
Tooth pain occurs when the nerve within the tooth root or near a tooth becomes irritated. Pain can also arise from:
-
Dental procedures, like extractions
-
Injury or trauma to the jaw
Sometimes, pain originates from nearby areas (ear, sinus, jaw) and radiates to the tooth, making it seem like a toothache.
Signs and Symptoms of a Toothache
-
Pain while chewing or biting
-
Swelling of the gums or jaw
-
Redness of the gums or jaw
-
Bleeding or foul-tasting discharge
-
Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks
Treatment / Management
-
Professional Dental Care:
-
Fillings or crowns for cavities
-
Root canal for infected tooth pulp
-
Tooth extraction if necessary
-
-
Pain Relief & Supportive Care:
-
Over-the-counter pain medications (e.g., ibuprofen, acetaminophen)
-
Cold compress for swelling
-
Saltwater rinse for gum irritation
-
-
Prevention:
-
Brush teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
-
Floss daily
-
Limit sugary or acidic foods
-
Regular dental check-ups
-
