Vestibular Disease
Vestibular Disorders
Overview
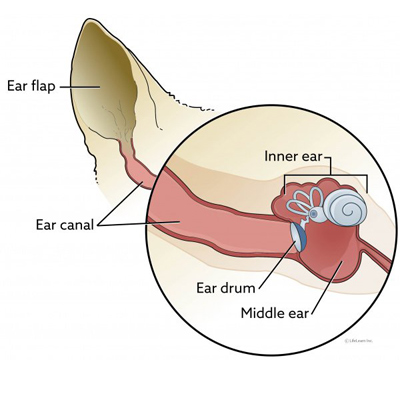
The vestibular apparatus includes structures in the inner ear and parts of the brain that process sensory information for balance and eye movements.
-
Damage to this system due to disease, injury, aging, or other factors can lead to vestibular disorders.
-
These disorders may also be influenced by genetic, environmental, or unknown causes.
-
Vestibular disorders affect the body’s ability to maintain balance, coordinate movement, and control eye motion, which can significantly impact daily life.
Symptoms
Vestibular disorders often present with one or more of the following:
-
Vertigo (a spinning or swaying sensation)
-
Dizziness or feeling faint/unstable
-
Balance problems leading to unsteadiness or falls
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Abnormal eye movements (nystagmus)
-
Hearing changes such as tinnitus or hearing loss
-
Difficulty focusing or visual disturbances
-
Sweating, headache, or fatigue associated with motion
Causes
-
Inner ear infections or inflammation
-
Meniere’s disease
-
Head injury or trauma
-
Age-related degeneration
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Unknown or idiopathic causes
Treatment / Management
-
Vestibular rehabilitation therapy to improve balance
-
Medications for dizziness, nausea, or underlying conditions
-
Lifestyle modifications (avoiding triggers, hydration, proper diet)
-
Surgical intervention in rare or severe cases