Geriatric depression
Geriatric Depression – Overview (Spaks Homeopathy)
Geriatric depression is a mental health condition that affects older adults, causing persistent sadness, low mood, and loss of interest in daily activities. While occasional feelings of unhappiness or “blue” moods are normal in aging, long-lasting depression is not a natural part of getting older.
Many elderly people may experience subsyndromal depression – a form of depression that does not meet the full criteria for major depression but can progress into severe depression if left untreated. Depression in older adults often goes unrecognized, as its symptoms may be mistaken for aging-related changes or physical illness.
Causes of Geriatric Depression
-
Loneliness and social isolation
-
Loss of spouse, friends, or family members
-
Chronic medical conditions (heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, stroke, etc.)
-
Long-term medication use (certain antihypertensives, steroids, or sedatives)
-
Reduced physical mobility or disability
-
Retirement-related lifestyle changes and financial stress
-
Family neglect or lack of emotional support
Symptoms of Geriatric Depression
-
Persistent sadness and low mood
-
Feelings of worthlessness or helplessness
-
Irritability and restlessness
-
Fatigue and loss of energy
-
Frequent crying spells
-
Apathy or lack of interest in activities
-
Disturbed sleep (insomnia or oversleeping)
-
Difficulty concentrating and making decisions
-
Physical symptoms like body aches and pains
-
Pacing, fidgeting, or nervous behavior
Effects / Complications
-
Reduced quality of life and loss of independence
-
Worsening of chronic medical conditions
-
Malnutrition due to loss of appetite
-
Increased risk of memory problems and dementia
-
Suicidal thoughts or self-harm in severe cases
Homeopathic Treatment for Geriatric Depression (Spaks Homeopathy)
Homeopathy offers a gentle, safe, and holistic approach to treating depression in elderly patients. Remedies help improve mood, reduce restlessness, and enhance overall well-being. Commonly prescribed medicines include:
-
Ignatia Amara – for depression with grief, mood swings, and frequent sighing
-
Aurum Metallicum – for hopelessness, sadness, and suicidal tendencies
-
Sepia – for apathy, indifference, and lack of interest in daily life
-
Natrum Muriaticum – for depression due to grief, loneliness, or past trauma
-
Phosphoric Acid – for depression with extreme fatigue, weakness, and lack of motivation
Note: Medicine selection must be individualized. Consultation with a qualified homeopathic physician is essential for effective treatment.

Headache-
Headache (Tension-Type Headache)
Overview
A headache is usually a diffuse, mild to moderate pain in the head, often described as a tight band around it.
The tension-type headache is the most common form, but its causes are not fully understood.
Treatment includes lifestyle changes, non-drug therapies, and proper use of medicines.
Symptoms
-
Dull, aching head pain
-
Sensation of tightness or pressure across the forehead
-
Tenderness in the scalp, neck, or shoulder muscles
Possible Effects if Untreated
-
Frequent or chronic headaches interfering with daily activities
-
Fatigue, irritability, and disturbed sleep
-
Reduced concentration and productivity
-
Risk of progression to chronic headache disorders
Homeopathic Treatment for Tension Headache
Homeopathy works on the root cause—whether stress, eyestrain, or digestive issues—and provides long-term relief without side effects.
Commonly Used Medicines
-
Belladonna – for sudden, throbbing headaches with sensitivity
-
Nux Vomica – for headaches due to stress, late nights, or indigestion
-
Bryonia Alba – for headaches worse on movement, better with rest
-
Natrum Muriaticum – for chronic headaches linked to grief or sun exposure
-
Gelsemium – for dull, heavy headaches with pressure feeling
Why Choose Spaks Homeopathy
-
Treats the root cause, not just symptoms
-
Safe and natural remedies without dependency
-
Personalized care for each patient
-
Expertise in headaches, migraines, and chronic conditions
Address: E-38, Budh Vihar, Badarpur, New Delhi – 110044
Phone: +91 8700458818
Email: info@spakshomeopathy.com
Spaks Homeopathy – Heal headaches naturally and restore balance to your life.

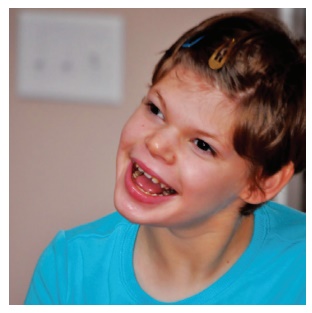
Hydrocephalus
Overview
Hydrocephalus is a condition where excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up in the brain’s cavities (ventricles). This causes the ventricles to enlarge and puts pressure on the surrounding brain tissues.
Normally, CSF flows through the brain and spinal cord, cushioning and protecting them. In hydrocephalus, the imbalance between fluid production and absorption leads to increased pressure, which can damage brain tissues and affect normal brain function.
The term “hydrocephalus” means “water on the brain”, though the fluid involved is CSF, not water.
Symptoms
In infants and young children:
-
Unusually large head
-
Rapid increase in head size
-
Bulging or tense soft spot (fontanel) on the top of the head
-
Poor growth and feeding difficulties
-
Irritability or drowsiness
-
Seizures
-
Eyes fixed downward (known as “sunsetting of the eyes”)
In older children and adults:
-
Headaches
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Blurred or double vision
-
Difficulty walking or balancing
-
Loss of coordination
-
Urinary incontinence
-
Decline in memory, concentration, or thinking ability
-
Weakness or stiffness in the muscles
Effects
If untreated, hydrocephalus can cause:
-
Brain damage due to sustained pressure
-
Developmental delays in children
-
Loss of independence in adults
-
Vision problems or blindness
-
In severe cases, life-threatening complications
Treatment
Hydrocephalus usually requires medical or surgical intervention.
1. Surgical Treatments
-
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt: A tube is placed to drain excess fluid from the brain ventricles into another part of the body (usually the abdomen).
-
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV): A small opening is created in the floor of the ventricle to allow CSF to flow more freely.
2. Supportive Care
-
Regular monitoring with brain imaging (MRI/CT scans)
-
Medications for symptom relief (anti-seizure drugs if seizures occur)
-
Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy to improve mobility and development
3. Homeopathic Supportive Treatment (under professional guidance only, not as replacement for surgery)
-
Helleborus niger – used for mental dullness and slow response linked to brain pressure
-
Apis mellifica – for swelling with drowsiness and irritability
-
Belladonna – when symptoms include headaches and vomiting due to raised pressure
Key Point: Hydrocephalus is a serious condition. With early diagnosis and proper treatment (usually surgery), many patients can live healthy, productive lives.
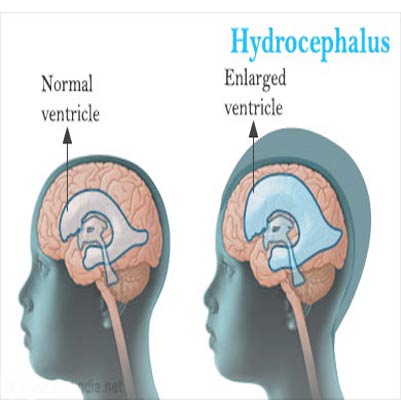
Ischemic stroke
Stroke (Cerebrovascular Accident – CVA)
Overview
A stroke is a serious medical emergency that occurs when blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. Brain cells begin to die within minutes.
There are two main types of stroke:
-
Ischemic Stroke – the most common type, caused by a blood clot or plaque that blocks blood flow to the brain. This may result from conditions such as arterial stenosis (narrowing of arteries due to atherosclerosis or coronary artery disease).
-
Hemorrhagic Stroke – caused by a blood vessel in the brain bursting and leading to bleeding, which damages nearby brain tissue.
A related condition is Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), sometimes called a “mini-stroke.” TIAs happen when blood flow to the brain is briefly blocked. Though temporary, TIAs are a warning sign of a possible future major stroke.
Symptoms of Ischemic Stroke
-
Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg (often on one side of the body)
-
Confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech
-
Sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or difficulty walking
-
Vision problems (blurred vision, double vision, or loss of vision in one/both eyes)
-
Severe headache (more common in hemorrhagic stroke)
-
Loss of coordination or sudden collapse
-
Permanent brain damage if not treated quickly
Stroke is a life-threatening emergency. Immediate medical attention can save brain function and reduce the risk of disability or death.
Hysteria
Hysteria
Overview
Hysteria is a psychological disorder that often develops as a defense mechanism to escape painful emotions. The distress of the mind is unconsciously transferred to the body, leading to both mental and physical symptoms.
It is characterized by sudden emotional outbursts, lack of control over emotions or actions, and sometimes convulsive seizures. The root cause is usually unresolved or repressed mental conflict.
Hysteria can occur in both men and women, but it is more common among young women between the ages of 14 and 25, as this age group is more sensitive to emotional stress.
Signs and Symptoms
Headache
Feeling of suffocation
Swelling of neck and jugular veins
Palpitations
Unconsciousness
Rapid heartbeat
Violent or jerky movements of the body
Clenched teeth
Emotional outbursts or crying spells
Effects
Interference with normal daily life and relationships
Increased anxiety and emotional instability
Frequent fainting or fits can lead to injuries
Difficulty in focusing on studies or work
Social withdrawal due to fear of sudden episodes
Homeopathic Treatment
Ignatia amara – for emotional outbursts, grief, and suppressed emotions
Stramonium – for violent behavior, fear, and convulsions
Lachesis – for talkativeness, jealousy, and fits with clenched teeth
Pulsatilla – for sensitive, weepy, and emotionally dependent patients
Hyoscyamus – for sudden jerky movements, restlessness, and suspiciousness

Kawasaki disease
Kawasaki Disease
Overview
Kawasaki disease is a condition that causes inflammation in the walls of medium-sized arteries throughout the body. It mainly affects young children, especially those under the age of 5.
The inflammation often involves the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle. Because it also affects lymph nodes, skin, and mucous membranes (in the mouth, nose, and throat), the disease is sometimes called mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important to reduce the risk of long-term complications, particularly heart problems.
Signs and Symptoms
-
Severe redness in the eyes (without discharge)
-
Rash on the stomach, chest, and genitals
-
Red, dry, cracked lips
-
Swollen tongue with a white coating and large red bumps (“strawberry tongue”)
-
Sore, irritated throat
-
Swollen, red palms of the hands and soles of the feet (often purple-red)
-
Swollen lymph nodes, especially in the neck
Effects
If untreated, Kawasaki disease can cause:
-
Coronary artery aneurysms (ballooning of arteries)
-
Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle)
-
Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats)
-
Long-term risk of heart disease
-
Irritability, joint pain, and fatigue
Treatment
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG): Given early to reduce inflammation and risk of heart damage
-
Aspirin: Helps reduce fever, pain, and prevent blood clots
-
Corticosteroids or biologic therapy: In resistant cases
-
Heart monitoring: Regular echocardiograms to check for coronary artery involvement
-
Supportive care: Rest, fluids, and monitoring of symptoms

Meningitisa
Meniere’s Disease
Overview
Meniere’s disease is a disorder of the inner ear that affects balance and hearing. It causes:
-
Episodes of vertigo (spinning sensation)
-
Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ear)
-
Hearing loss
-
A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
It usually affects one ear. The attacks may come on suddenly or after a short period of muffled hearing or ringing. Some people experience rare, isolated attacks, while others may have several episodes close together over a few days.
In severe cases, people may lose balance suddenly and fall without warning. These episodes are called drop attacks.
Symptoms
-
Repeated episodes of vertigo (dizziness with spinning sensation)
-
Vertigo lasting 20 minutes to several hours (but less than 24 hours)
-
Severe dizziness causing nausea or vomiting
-
Hearing loss (may come and go early but can become permanent over time)
-
Tinnitus – ringing, buzzing, roaring, or hissing sound in the ear
-
Fullness or pressure in the affected ear
Effects / Complications
If untreated or progressive, Meniere’s disease may cause:
-
Permanent hearing loss in the affected ear
-
Frequent vertigo attacks leading to imbalance and falls
-
Drop attacks (sudden falls without warning)
-
Emotional stress, anxiety, and depression due to unpredictable attacks
-
Reduced quality of life from ongoing dizziness and hearing problems
Treatment
Medical / General Treatment
-
Dietary changes (low-salt diet, avoid caffeine and alcohol)
-
Diuretics (to reduce inner ear fluid buildup)
-
Vestibular suppressants (meclizine, diazepam) during vertigo attacks
-
Anti-nausea medicines (promethazine)
-
Hearing aids for permanent hearing loss
-
In severe cases: injections or surgery (for persistent vertigo not controlled by medicines)
Homeopathic Supportive Remedies (to be used under guidance of a qualified homeopath)
-
Cocculus indicus – for vertigo with nausea and weakness
-
Gelsemium – for dizziness with heaviness and trembling
-
Conium maculatum – for vertigo worsened by turning the head or lying down
-
China (Cinchona officinalis) – for tinnitus with sensitivity to sound
-
Phosphorus – for progressive hearing loss with ringing in the ears
This structure covers Overview → Symptoms → Effects → Treatment (Modern + Homeopathy) in simple and clear English.
Mental Retardation
Intellectual Disability (Mental Retardation)
Overview
Intellectual Disability (ID), previously known as mental retardation, is a condition where a child’s brain does not develop properly, leading to limitations in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior (daily living, social, and practical skills).
-
Children with ID can learn and develop skills, but they do so more slowly than others.
-
The condition varies in severity — from mild to profound — and affects learning, communication, reasoning, and independence.
Symptoms
-
Developmental delays: sitting, crawling, or walking later than peers
-
Difficulty learning to talk or unclear speech
-
Low IQ (below 70)
-
Memory problems
-
Inability to understand consequences of actions
-
Difficulty with logical thinking and problem-solving
-
Behavior that seems younger than the child’s age
-
Lack of curiosity and limited interests
-
Ongoing learning difficulties in school and daily life
Effects / Complications
-
Academic challenges – slow progress in school, difficulty understanding concepts
-
Social difficulties – trouble forming friendships, poor communication skills
-
Emotional stress – frustration, low self-esteem, dependence on others
-
Independence issues – difficulty performing everyday tasks without support
-
May be associated with other conditions like ADHD, autism, seizures, or sensory impairments
Treatment & Management
Medical & Supportive Care
-
Early intervention programs – speech therapy, occupational therapy, special education
-
Behavioral therapy – to improve communication, social skills, and adaptive behaviors
-
Medications – for associated conditions (e.g., seizures, hyperactivity, mood issues)
-
Skill training – focus on self-care, vocational, and life skills for independence
-
Parental counseling & support groups – to guide families in handling challenges
Homeopathic Supportive Remedies (under expert guidance)
-
Baryta Carbonica – for delayed development, shyness, and learning difficulties
-
Calcarea Phosphorica – for slow growth, weak memory, and late milestones
-
Tuberculinum – for restless children with poor concentration and irritability
-
Silicea – for children who are timid, slow learners, and lack confidence
-
Bufo Rana – for profound intellectual disability with behavioral issues
This covers what intellectual disability is, its symptoms, effects, and both medical & homeopathic approaches.